Big storm broke out on the sun
Radio communication on Earth interrupted for a short time after a strong outbreak occurred on the solar layer of the sun.
Storm burst from the black spot AR 11598 - a strong active area of the sun. The intensity of the storm reaches the maximum level at 3:05 am on October 22 at GMT, 10h22 on the same day in Hanoi. Solar Dynamics Observatory, an artificial satellite launched by the US Aerospace Agency (NASA) to monitor the sun, has discovered a storm. The US Space Weather Forecast Center said that this is a level X1.8 storm - that is, the most powerful solar storm group.
After the storm broke out, charged particles from the sun rushed to Earth and paralyzed the radio signal for a short time, Space reported.
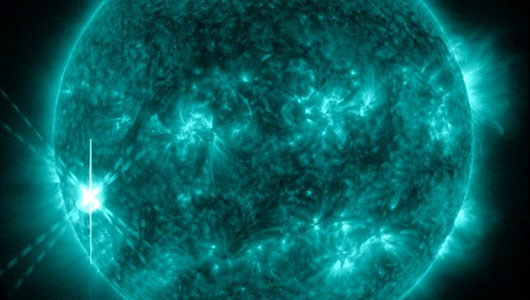
A photo taken by Solar Dynamics Observatory satellite
shows that the storm erupted from the black spot AR 11598 on October 22.
Black Point AR 11598 once created three powerful storms within two days since it became the target that humans could observe from the earth.
"That means strong storms will continue to come from that black spot. Because of the black point towards the earth in the coming days, the solar storms will increasingly head towards us , " Tony Philips , an astronomer from spaceweather.com, said.
Black stains are dark areas on the surface of the sun. They appear due to strong magnetic changes. The brightness of the black spot is only 1/4 of the brightness of the surrounding area. Strong solar storms often appear from dark spots and they release streams of charged particles into space.
The scientific world divided the solar storm into three levels C, M and X, where X is the strongest. Solar storms of level X can cause storms from the planet's upper layer. The interaction between charged particles from the sun and the earth's magnetic field can cripple radio waves. M-level solar storms can cause radio signal loss in the two polar regions of the earth for short periods of time. The impact of Class C solar storms is often very small and rarely detected.
- Strange storm broke the whole city in 1674
- Hurricane 6 suddenly turned, headed into the Gulf of Tonkin
- 'The first time he broke his forehead', broke the TV because of Nintendo Wii
- Breaking many dykes in the Mekong Delta
- Tin latest storm No. 3: Lightning storms landed in Hai Phong - Ninh Binh
- Storm No. 15 has not melted, near the East Sea, a new storm appears
- Tropical depression strengthened into storm No. 2, heading to Quang Ninh - Hai Phong
- Storm Dianmu accelerated, Hanoi prepared to catch a storm
- Why is storm No. 10 the first storm in Vietnam to be warned red?
- Standing still for 24 hours, storm No. 4 is about to accelerate
- Cyclone storm, typhoon typhoon and storm tropical storm What's the difference?
- Photo: Super typhoon Yutu caused heavy damage when landing in the Philippines
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people Which planet is the largest in the Solar System?
Which planet is the largest in the Solar System?  The Sun goes into hibernation, will the Earth usher in a new ice age?
The Sun goes into hibernation, will the Earth usher in a new ice age?  263 extrasolar objects discovered, hinting at a mysterious belt outside the Kuiper Belt
263 extrasolar objects discovered, hinting at a mysterious belt outside the Kuiper Belt  Does the Solar System have 5 more planets similar to Earth?
Does the Solar System have 5 more planets similar to Earth?  Superstructure in space 'shades' Earth
Superstructure in space 'shades' Earth  US successfully transmits solar power from space to Earth
US successfully transmits solar power from space to Earth 