Brown stars are the third cosmic object after stars and planets
The system for classifying cosmic objects is in need of adjustment. Researchers at the Argelander Astronomical Institute at Bonn University have discovered that brown stars need to be separated into a new star and planetary group.
So far, brown stars are considered smaller stars than usual. However, that could be the 'miscarriage' of the star.
Brown stars (or BD) are called by scientists to reside in the nearby galaxy. Unlike stars, they cannot produce as much melted hydrogen as the center of the sun because of their size (about 8% smaller than the sun). In addition, brown stars and stars seem to be different in 'making partners'.
Stars often go into pairs, dance around each other. However, this activity is very diverse: sometimes the distance between two stars is smaller than the radius of the earth orbit (also called astronomical or AU). However, a pair of stars can be separated by up to 1000 AU. "Everything is completely different from brown stars. The orbital radius of a pair of brown stars is only about 15 AU, pairs of brown stars with roughly the same distance," explains astrophysicist Ingo Thies of Bonn . the farther is the exception '.
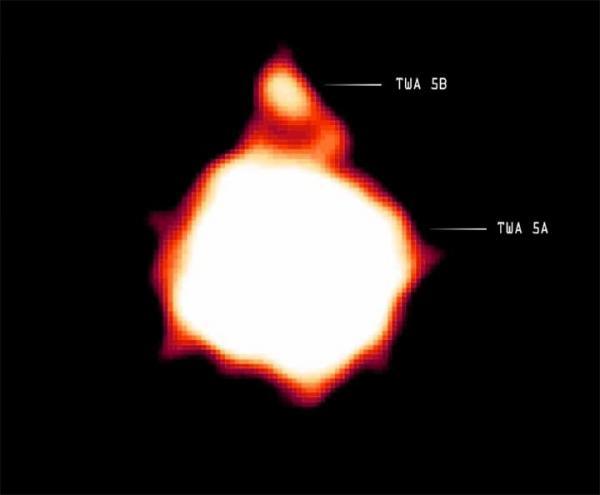
X-rays produced by TWA 5B, a brown star travels in the orbit of a young two-star system called TWA 5A (Photo: NASA / CXC / Chuo U./Y. Tsuboi et al.)
In addition, there are almost no pairs of sun and brown stars - much less expected. This phenomenon is called brown star dryness. Professor Pavel Kroupa of Argelander Academy explains: 'According to the classical model, there should be no differences. According to this theory, both brown stars and stars that appear from interstellar gas clusters become concentrated because of their attraction from their size. But if this is the case, these cosmic objects must work similarly. '
Despite this contradiction, the astronomical community always maintains the theory of the common origin of objects. However, Ingo Thies and Pavel Kroupa have for the first time proposed that brown stars must be viewed as a separate type of object. Ingo Thies explained: 'We studied the size of the newly emerging stars. This shows a jump in the size distribution that creates the interstellar division '.
The death of an embryonic star
So how is brown star born? In 2001, Danish researcher Bo Reipurth, along with British astronomer Cathie Clarke and Spanish astronomer Eudardo Delgado-Donate, had the idea that brown stars could be understood as 'miscarriage'. ' star ' : the system consists of 3 stars in the embryonic stage that decompose because of mutual attraction, and the smallest object is pushed out of the system . This physical mechanism has long been known: even Pioneer and Voyager probes were pushed into a trip that did not return because of planetary gravity.
Another possibility is that brown stars create a peripheral region of new stars that appear and are separated from them. This may be the result of a third star encounter. Since most stars are born in a cluster, such meetings are not rare. It is also possible that both cases of 'miscarriage' in the universe occur.
Both theories predict that brown stars occur during star formation - similar to the planet's case. So there may be three different cosmic objects: planets, brown stars, and stars.
Refer:
Thies, P. Kroupa.A discontinuity in the IMF - the case of high multiplicity.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 20 Aug 2008
- How brown stars form
- Brown stars don't go with normal stars
- Stars change color when swallowing the planet
- Learn the formation of the planet through
- Discover the planet has the three Suns closest to Earth
- The most exotic new planets 2012
- Take a photo of two sun planets
- First recorded the 'eating' planet image around the young star
- Discover more 18 large planets
- Detects two gas planets orbiting the star
- The most frightening 'monsters' in the universe
- The mysterious planet causes the orbiting star to age
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people NASA discovers two stars colliding so violently that they created gold
NASA discovers two stars colliding so violently that they created gold  James Webb Telescope Discovers Massive Supercluster Hidden Deep in the Milky Way
James Webb Telescope Discovers Massive Supercluster Hidden Deep in the Milky Way  'Time travel' 13.5 billion years, NASA telescope finds 4 cosmic ancestors
'Time travel' 13.5 billion years, NASA telescope finds 4 cosmic ancestors  Why there are no stars in American photos of the Moon
Why there are no stars in American photos of the Moon  Aliens control the fastest moving stars in the galaxy?
Aliens control the fastest moving stars in the galaxy?  First 'hybrid' star and planet object revealed outside the Milky Way
First 'hybrid' star and planet object revealed outside the Milky Way 