Computer network models
A computer network is a system of multiple computers and devices connected by a physical link to an architecture (Network Architecture) to collect, exchange data and share resources for many user.
An online computer can be one of three types as follows:
- Client (Client) :Does not provide resources but only uses resources from the network.
- Server (Server):Provides resources and services for machines on the network.
- Peer :Using resources and also providing resources for the network.
Based on how computers are connected to the network as well as how they interact with the network and each other, computer networks are divided into three basic models as follows:
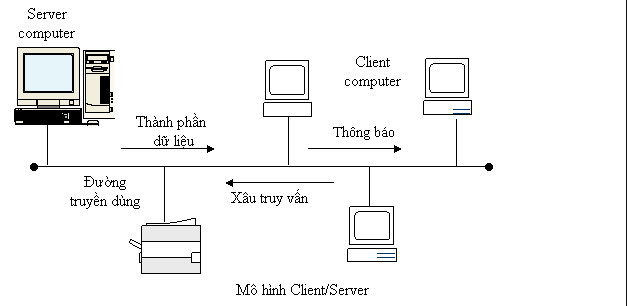
Station-master model (Client-Server)
Workstations are connected to servers, receive network access and network resources from servers. For Windows NT machines are organized into domains (domains) . Security on domains is managed by some special servers called domain controllers. On a domain that has a master domain controller is called a PDC (Primary Domain Controller) and a BDC (Backup Domain Controller) in case PDC goes down.
Client / Server software model is a software solution model for overcoming network overload and overcoming differences in physical structure as well as operating systems of computer systems. different online.
Each software built under the Client / Server model will be divided into two parts: the part operating on the server is called the Server side and the part operating on the workstation is called the Client side. With this model, workstations are also called clients (or client machines) and servers are called servers. The duties of each section are defined as follows:
- The Server side manages the external environment communications at the Server and with the Client, receives requests in the form of strings (query string), analyzes query strings, processes data and sends the returned results. words on the client side.
- The Client side organizes communication with the user, with the external environment at the workstation and on the Server side, receiving user requests, establishing query strings to the Server, receiving results and organization. show them.

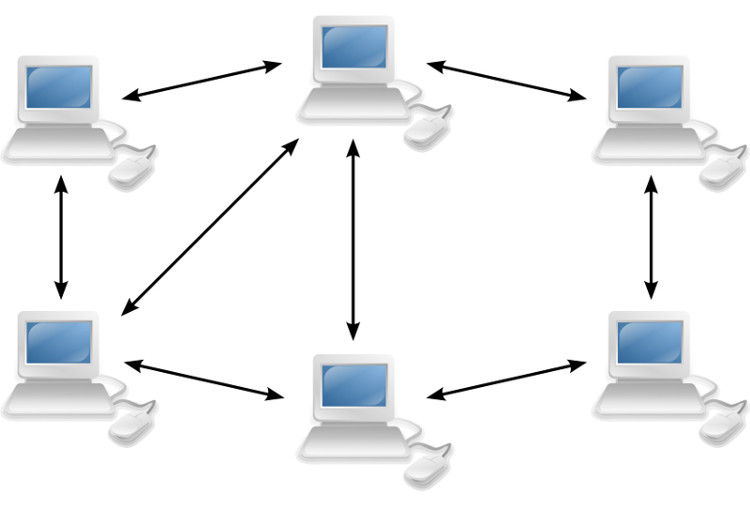
Peer-to-Peer model (Peer-to-Peer)
Peer network (p2p) is a network in which two or more computers share files and access devices such as printers without the need for a server or server software. Peer networks are often organized into workgroup workgroups. This model does not have a central login process. If you are logged in, you can use all resources on the network. Access to resources depends on who shared the resources, so you may need to know the password to gain access to the shared resources.
The p2p network is created by two or more computers that are connected to each other and share resources without having to go through a dedicated server. The p2p network can be connected on the spot - two computers connected via USB to transfer files. P2 can also be a permanent infrastructure that connects 5-6 computers together in a small office with copper cables. Or it could be a much larger network, using special protocols and applications to establish direct relationships between users on the internet.
Peer-to-peer computer network model.
Hybrid model (Hybrid)
This model is a combination of Client-Server and Peer-to-Peer. Most computer networks actually belong to this model.
In the above network models, each model has its own advantages and disadvantages for each evaluation criteria such as information security, installation, network scalability . Comparison between The above network models for some common evaluation criteria are given in the following table:
Network model
Client-Server
Peer-to-Peer
Hybrid
Evaluation criteria
Safety and information security.
The highest level of security and information security.Network administrators can adjust access to information.
Poor security and security, depending on the level of shared access.
High security and security almost as Client-Server.
Installation capability.
Difficult to install.
Easy to install.
Difficult to install.
Requires hardware and software.
Requires server, network operating system and additional hardware.
No server, network operating system needed, very little additional hardware.
As Client-Server.
Network administrator.
Must have network administrator.
No need for network administrators.
As Client-Server.
Processing and centralized storage.
Have.
Is not.
Is not.
Installation costs.
High.
Low.
High.
- Installing and configuring the 2004 ISA Server Firewall - Chapter 4
- Self-troubleshooting network system thanks to artificial intelligence
- A new dangerous network spy tool appears
- Causes and ways to fix computers not on Facebook
- See Earth from 430km altitude right on your computer
- Spiceworks Desktop - A great help for network administrators
- The Internet is under water
- The most dangerous computer viruses of the time
- See network security struggles like the front
- Create LAN over the Internet with Hamachi
- Russia: The computer failed to make ISS space station stand
- Computer made from slime mold
 What is the Snapdragon SiP chip?
What is the Snapdragon SiP chip? How to create a yellow circle around the mouse cursor on Windows
How to create a yellow circle around the mouse cursor on Windows Edit the Boot.ini file in Windows XP
Edit the Boot.ini file in Windows XP 3 ways to restart the remote computer via the Internet
3 ways to restart the remote computer via the Internet