Cool the planet by planting the right plants
By carefully selecting food crops, it is possible to reduce temperatures in most of Europe and North America to 1 ° C during the summer season, researchers from Bristol University, UK said. This is equivalent to reducing the annual global temperature to 0.1 ° C, equivalent to 20% of global temperatures since the Industrial Revolution.
Crop development creates a cooling effect on the climate because they reflect sunlight back into space. Different types of plants have a significant difference in light reflection, so selecting those plants that are more reflective will support this cooling effect. Since cultivation is a global industry, the cooling effect will be wide-ranging.
Dr. Andy Ridgwel and colleagues at Bristol University argue that we should choose suitable crops to be able to control somewhat climate, in the same way we are currently cultivating crops to maximize real output.
Dr. Ridgwel said: 'We have assessed the impact of this method on the global climate model. By selecting certain crops, an appreciation of the reflectivity increases leading to our prediction that summer temperatures will be reduced by more than 1 ° C in the North American central region and the latitude. Central Asia region. The impact of regional climate cooling can be done through selection of varieties or genetic modification to take advantage of the plant's ability to reflect light. '
The research team stressed that unlike planting biofuel crops, this plan could be implemented without affecting food production. Ridgwell explains: 'We have to choose different varieties of the same crop to maximize the ability to reflect the light of that crop, not to change the type of plant, although that way is also may bring certain benefits to the climate '.
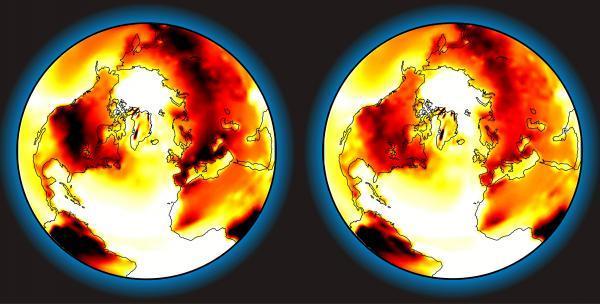 The cooling effect of growing sun-reflective crops in the next 100 years.The image on the left shows the predicted increase in temperature at the end of the century, due to CO2 concentrations doubling.The image on the right shows the cooling effect of looking at the sun reflecting trees.Color ratio: white = 2 warmth (or less) to black = 8 warming (or more).
The cooling effect of growing sun-reflective crops in the next 100 years.The image on the left shows the predicted increase in temperature at the end of the century, due to CO2 concentrations doubling.The image on the right shows the cooling effect of looking at the sun reflecting trees.Color ratio: white = 2 warmth (or less) to black = 8 warming (or more).
In the next hundred years, these decisions are equivalent to preventing 195 billion tons of CO2 released into the atmosphere. Farmers should be encouraged to cultivate those crops by issuing carbon credits. Ridgwell calculated that if this mechanism were implemented, farmers would earn 23 euros per hectare per year. Biofuel crops currently earn 45 euros a year, but waste a valuable agricultural land needed for growing food crops.
Plants differ in their ability to reflect sunlight because of differences in the properties of leaf surfaces and the distribution of leaves. The research team therefore proposed that crops should be selected based on light reflection properties along with other considerations such as the ability to process the actual quantity of a variety.
Because society is still unwilling to reduce the use of fossil fuels to reduce the release of carbon dioxide, there are simple alternatives such as planting more crops that can reflect high sunlight. is a practical method to reduce the severity of heat waves and droughts.Results can be achieved in a short time at a very low cost.
Ridgwell commented : 'Still more research is needed on the diversity of the ability to reflect sunlight that exists between different types and varieties of plants. We are looking for funding to be able to determine possible quantities, diversity for future breeding, and whether genetic modification measures are needed. '
Refer:
Andy Ridgwell, Joy S. Singarayer, Alistair M. Hetherington and Paul J. Valdes.Tackling Regional Climate Change by Leaf Albedo Bio-geoengineering.Current Biology, January 27, 2009
- Sa Pa: Planting medicinal plants for medicine
- Techniques for planting rare and precious milk plants
- Crops help the house cool on hot days
- Method of planting a cool military flower truss in the summer
- Planting trees may not cool the earth
- Mistakes when planting many plants and flowers in the room
- Techniques for fertilizing ornamental plants, ornamental flowers
- Do you have to remove potting covers when planting trees?
- Technical planting and care of Thai porcelain
- Technical guidance on planting and caring for geraniums
- Planting bonsai by hydroponic method
- Instructions on how to grow squash for high productivity
 Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity?
Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity? Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer
Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer Lightning stone - the mysterious guest
Lightning stone - the mysterious guest Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance
Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance