How does NASA solve food problems in space?
Eating a nutritious diet was not simple for us and it was much more difficult for cosmonauts in the universe, where all human life activities became 'unusual'. NASA recognizes that this is a problem full of difficulties to be solved but if successful, it will create tremendous motivation for people to go further into the universe, to achieve even greater discoveries. So what did they do to solve human food problems in the universe?
How to solve food problems for NASA astronauts
It is said that when he began his four-year world expedition, Admiral George Anson brought a crew of 2,000, but less than half when he returned. Most die on the road because of scurvy and the main cause is a deficiency of vitamin C. Hearing the story seems serious, but according to Scott Smith, a dietitian at NASA, that is still too simple compared to What they have to deal with in the universe.
For long journeys in the future, astronauts must bring all their own food and they must contain the right amount of vitamins and minerals they need.'In a three-year mission, the lack of a nutrient can lead to poor mission endings.' So, Smith and colleagues at the Johnson Research Center, NASA, think that if you solve the problem of nutrition in the universe, it will help people go a step further in the universe, most notably Mars. .
On ISS, what do astronauts eat?
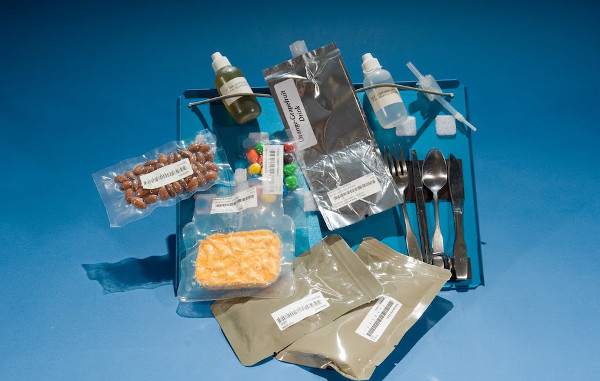
A meal for astronauts in space.
Currently, astronauts working on the ISS international space station will often eat 8 times a day. Most of the meals are mostly in liquid form or military MRE food packages that are contained in plastic bags (prepared foods with beef, chicken, teriyaki, etc.). There are also common packaged foods that can be purchased at stores below Earth such as almonds or brownies. Hot and cold drinks are all contained in straw bags. The food is attached to the velcro kitchen area to prevent it from flying around.
Smith said astronauts often complain about their meals: Although food tastes like the Earth, most don't need to chew! Sandra Magnus, a NASA engineer, proposed the idea of using corn bread crumbs to make it into other food items in the space: 'I think anything can be added with corn bread'. By developing a complex cooking system with recycled plastic bags, cutting boards and mixing tools, she can mix food with garlic and onion with olive oil and keep it warm for up to 4 hours.
Likewise, astronaut Sunita Williams in missions Expeditions 14, 15, 32 and 33 made salmon macaroni noodles by mixing salmon bags with pasta to moisten and cheese. Food is transferred from Earth to resupply the space station 6 times per year. However, that distance is still very close and NASA wants to find solutions for further missions: Mars.
Food standard Mars: nutritious, stored for 5 years while still ensuring quality

NASA has long prepared everything to serve the Martian mission, scheduled to be deployed in the 2030s. The journey to Mars will take between 2.5 and 3 years. According to an estimate in 2012, the trip needs to bring 12 tons of food to serve 6 astronauts and that is just the amount of food, not to mention packing, storage, .
So, instead of putting it once, NASA plans to break down the food, using other spacecraft to move to Mars before the astronauts depart. Therefore, scientists must find ways to preserve such food must be used after 5 years. On the other hand, putting ingredients on Mars so that the astronauts cook themselves will make them easier to live, less lonely and more homesick.
In addition to ensuring rations on intake, NASA also needs to ensure adequate nutrition for astronauts. There are some types of nutrients that will disappear over time. In space with full of cosmic rays, radiation types, . the problem will be even more serious. On the other hand, eating in weightless conditions, shrinking bones, . is not a small challenge. And more importantly, food must be attractive enough for astronauts to eat, making sure to provide the energy they need. If they do not eat enough, they will not have muscle energy, not enough intelligence to face problems arising in space.
In a biochemical study, NASA used two copper-spotted astronauts Mark and Scott Kelly to explore the challenges they face. Currently, Scott is in the middle of a one-year mission on ISS and his brother Mark still lives below the Earth. During this time, researchers closely monitored the metabolism, cardiovascular, microbiological and psychological health of both people for comparison. At the same time, the study also took samples of urine and blood of other astronauts for additional control.

A meal on the universe.
From the data collected, NASA will determine the link between nutritional deficiencies and physical health problems.Basically, the muscles and bones of astronauts will be withdrawn in space. Exercise is not the best way to solve the problem. Recent studies have shown that astronauts' bodies contain too much iron and that reduces the rate of bone. Therefore, nutritional changes can help solve this problem. Specifically, astronauts who eat a lot of fish will have a lower degree of musculoskeletal decline than others.
On the other hand, some astronauts suffer from vision loss and squint their eyeballs after long journeys over space. The reason is that the fluid inside the eyeball moves abnormally under zero gravity conditions. However, according to a recent study by Smith, nutrition is also one of the causes: astronauts with vision problems differ in the gene trait that regulates folic acid and vitamin B12 treatment. .
After solving the nutritional balance problem in food, another thing is equally important to ask NASA to solve the problem: to keep the food usable after 5 years . Typically, Vitamin C in food is easily lost. Once, NASA stored food for a year and then tested it, Vitamin C, A, Folic Acid and thiamin were lost.
Currently, despite trying a lot of processing techniques with a variety of foods, from drying to freezing, NASA has yet to find a way to keep food for 5 years while still ensuring quality. On the other hand, NASA does not want to use drugs to supplement vitamins. The reason is that depending on the type of food, the medicine that the human body will have different tolerances, so when astronauts take the medicine, they will feel less want to eat real food. In other words, too little nutrition is not possible but too much is not done. Only vitamin D is required to take medication because astronauts cannot reach enough sunlight to produce vitamin D in the usual way.
How to fit on a helmet to eat?

Not only does NASA pay attention to the amount of nutrients in food, but NASA also cares about how astronauts eat. Thinking about long-term missions, tasks that are required to work for hours or even a few dozen hours in Mars space suits, how can astronauts eat and drink normally?
In the first missions, NASA equipped a fruit bar inside the astronaut's clothes to make fast food. But astronauts often don't pay attention to them. Currently, the inside of the suit is only available to drink. In the future, NASA is trying to equip a 'connector' and straws on a helmet to bring food in when astronauts are working.
Another solution seems to be more feasible than developing a new set of clothes that can be attached to self-propelled vehicles in space, when astronauts can take off protective gear and get inside the car to dine.
Astronauts become farmers
The solution of planting trees on spacecraft or on other planets may solve part of the problem. Astronauts don't need to carry too much food from Earth. Instead, they will plant and feed themselves with vitamin-rich fresh vegetables. At the same time, they will have enough materials to coordinate the various menu of food.

Sample of long leaf lettuce grown on the International Space Station ISS.
Last August, astronauts ate fruit for the first time. Currently, they have grown long-leaf lettuce grown under the purple light (this is actually the second crop, and the first one was sent to Earth to test whether it is safe to eat) . In a video, astronaut Kjell Lindgren used scissors to cut lettuce leaves, then soaked in oil, vinegar and sandwiched with bread to eat. Great!
Not only that, NASA scientists are continuing to find ways to grow more types of agricultural products such as tomatoes, peppers and even dwarf plums. From this success, they hope that the first people to Mars not only cultivate fruits and vegetables but also grow food crops like wheat, .
However, it is not easy to turn an astronaut into a farmer and it takes time, experience and equipment to ensure that wheat is grown, then turn it into bread. . But if successful, this will initially improve the quality of astronauts' meals, further going to Mars on self-sufficiency in the future.
The food is not only nutritious, it needs to be beautiful and has an attractive taste

However, the biggest problem to be solved is to help astronauts want to eat and eat enough . How can they swallow attractive foods if the body is tired, stressed by overwork? Understanding that, NASA continued to approach the problem in terms of psychology. They study the transformation of taste and smell in a zero gravity and isolated environment.
In one study, scientists asked astronauts to fill out a questionnaire about their moods before and after eating. At the same time, the crew was asked to evaluate the quality of the meal, the cooking experience, and so on. In this way, NASA believed that it would find a way to create the perfect dish, while ensuring nutrition and creating life. The spirit for astronauts on long-distance journeys in space. Therefore, coffee and some types of breakfast are as important as other main foods.
- Find the solution to one of the most difficult math problems
- The prize was awarded to the postman on the board, winning 1 million dollars in bonuses
- NASA organizes software tests that can be applied in the universe
- Man can solve problems in the unconscious
- From chaos to order: How to find food?
- NASA postponed the mission to explore Mars
- Japan developed robots to know Todai university math problems
- NASA makes pizza with 3D printer
- Speak loudly to solve problems faster
- If you solve this puzzle, you are even better than an architect
- Things you didn't know about NASA
- Program to expand living space on the ISS station has problems
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people Why did American astronauts have to be quarantined when returning to Earth?
Why did American astronauts have to be quarantined when returning to Earth?  How to get back to the spacecraft if the astronauts leave the cabin to work and accidentally drift away?
How to get back to the spacecraft if the astronauts leave the cabin to work and accidentally drift away?  'Super Limbs' invention helps astronauts stand firmly on the Moon
'Super Limbs' invention helps astronauts stand firmly on the Moon  Close-up of NASA's new lunar exploration rover
Close-up of NASA's new lunar exploration rover  Spider-legged backpack pulls astronaut to his feet on the Moon
Spider-legged backpack pulls astronaut to his feet on the Moon  To stay healthy while working on the Moon, astronauts can use the Wall of Death
To stay healthy while working on the Moon, astronauts can use the Wall of Death 