Most amphibians can glow in the dark
Amphibians that can glow in nature are not uncommon as many people think.
In a study published February 27, scientists Jennifer Lamb and Matthew Davis of St Cloud State University in Minnesota said they exposed 32 species of frogs, salamanders, newts and eels. with blue or ultraviolet light, and discovered that these organisms emit colorful patterns in a process called "bioluminescence". These patterns are very diverse from spots and stripes with many colors such as green, orange and yellow. Some even have skin excretion and fluorescent green urine.
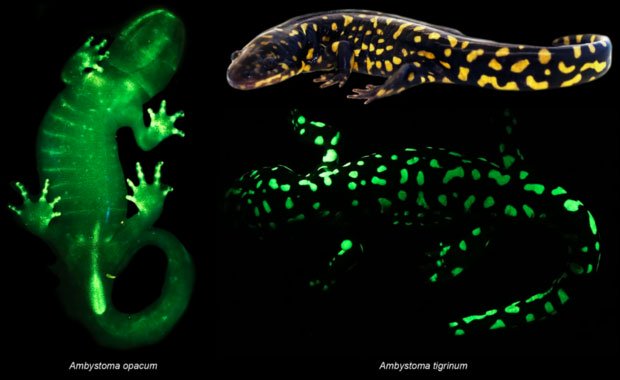
Fluorescent models vary depending on the variety and body type of a salamander.
(Photo: cbsnews.com).
Bioluminescence allows the organism to emit light after absorbing the first light energy. This process occurs through various mechanisms thanks to the presence of fluorescent proteins that exist in the skin and bones. Some amphibians also have chromosomes, or contain pigments and light-reflecting cells.
According to scientists, many amphibians are nocturnal and mainly concentrated in forests. Therefore, the ability to glow can help them find each other, as their eyes contain rod-shaped cells that are sensitive to green or blue light. Bioluminescence can also create a greater contrast between amphibians and their habitats, allowing other amphibians to easily recognize each other.
Bioluminescence is also recognized in some other species, helping them to camouflage, hunt or find mates. For example, jellyfish take advantage of this special ability to prevent predators. Meanwhile, the flickering light emitted at the tail of the adult fireflies is the " dance" that invites the mates of this creature.
- Found fish-like creatures that glow in the dark
- Sharks have a unique ability to emit green light
- Smart highways
- Cats glow in the night
- The world knows almost two-thirds of amphibians
- Amphibious species take their skin ... feed me
- The strange mushroom glows in the dark
- Glow pig is born in China
- Bunch of toxic, strange and rare amphibians in the world
- The number of amphibians decreases due to fungal infections
- New report on mass extinction events in amphibians
- New explanation of the origin of dark matter
- Mysterious red orange glow on the Pacific Ocean
- Trees glow themselves in the dark
 Animal 'suffering' after hibernation
Animal 'suffering' after hibernation Why do goats climb well?
Why do goats climb well? Scientists were surprised to see chimpanzees eating turtles
Scientists were surprised to see chimpanzees eating turtles Giant catfish died deadly due to drought in Thailand
Giant catfish died deadly due to drought in Thailand