November 17, 1967 - The first object takes off from a place outside of Earth
After 10 days of a lunar survey, on November 17, the rocket engine on Surveyor-6 was active for 2.5 seconds, the spacecraft flew to an altitude of nearly 4 meters, then landed for a second time. 2 down to the position about 2.4m away.
November 17, 1967 - NASA's Surveyor-6 spacecraft becomes the first object to take off from a place outside of Earth
Surveyor-6 is a NASA landing-type exploration ship, carrying out a soft landing process on the Moon, filming, taking photos and conducting some chemical analysis. The spacecraft weighs 299.6 kg, operating on solar energy. Launched on November 7, 1967 by the Atlas-Centaur missile system , Surveyor-6 took nearly 3 days to fly to the Moon. On November 10, the spacecraft successfully landed softly into the Sinus Medii area halfway to Earth's Moon.
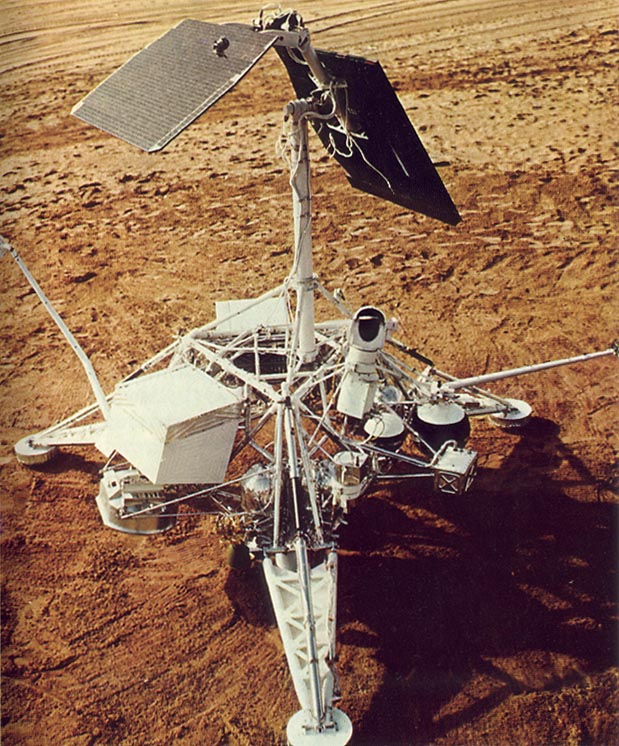
Surveyor-6 Ship.
After 10 days of a lunar survey, on November 17, the rocket engine on Surveyor-6 was active for 2.5 seconds, the spacecraft flew to an altitude of nearly 4 meters, then landed for a second time. 2 down to the position about 2.4m away. Although it took only a very short time, this second take-off helped scientists check the process of boosters on the lunar surface (preparing for manned expeditions). under Apollo program). Surveyor-6 continues to work effectively on the Moon until November 24. The final ground signal also received from Surveyor-6 is on December 14, 1967.
The NASA Surveyor program was conducted between 1966 and 1968. 7 automatic exploration ships landed on the Moon with the main purpose of preparing for the process of conquering this celestial body with Apollo ships . The main task of the program is to test the spacecraft's soft landing techniques on the Moon. Besides, on Surveyor ships, it is also deployed to analyze and evaluate components and structure of rock on the surface of the Moon to check the feasibility of bringing people to land on celestial bodies. this. All 7 Surveyor ships successfully approached the Moon, however two Surveyor-2 and Surveyor-4 ships encountered a late defeat and were destroyed when crashing into the Moon. The remaining 5 ships successfully rolled down as planned. So far, Surveyor ships are still on the Moon, only part of Surveyor-3, brought back to Earth by the Apollo-12 crew.

Surveyor-3 Ship.
Surveyor ships are shaped like a rack with three legs, on which equipment and machinery are deployed. Spacecraft is about 3.3m high, calculated from the middle to the end of each leg about 4.3m long. Energy to maintain operation is mainly provided from a 0.855 square meter solar panel, a capacity of about 85 watts. Surveyor ships were launched to the Moon using the Atlas-Centaur missile system. During the landing, the brake missile was activated until the spacecraft was only about 3.5 meters away from the surface. At this height, the offensive missile and Surveyor will fall freely to the Moon. Observations and analyzes will be conducted immediately after successful soft landing.
The final task in the Surveyor program was conducted in early 1968. On January 7, Surveyor-7 was launched toward the Moon. Compared to the previous ships, Surveyor-7 carries more observing, analyzing equipment and does not conduct research on jet engine operation on the Moon such as Surveyor-5, 6. January 10 / 1968, Surveyor-7 successfully landed on the southwestern side of the Moon, at the outer edge of the Tycho region. Everything happened as planned, the amphibious ship worked effectively until it was turned off on January 26, 1968, ending the first working day on the Moon (January 26, 1968). February 12, Surveyor-7 is turned on again and continues to work until February 20. The goals set for the mission are completed. Surveyor-7 successfully closed the program of automatic amphibious launches preparing people to set foot on the Moon in the 1960s of the United States.
- The mysterious artificial flying object is about to crash into Earth?
- Photo of Earth when eclipse occurred from the Moon
- Close record of Jupiter-Earth: September 20, 2010
- 'Reveal' the most favorable place for aliens to observe the Earth
- Google Earth takes a black circular object like a flying saucer
- When the spacecraft is mistaken for a meteorite near Earth
- Astronauts bring cosmic flies to Earth
- Will the Earth sink into darkness from November 15-29?
- Revealing the mysteries of the Earth makes everyone 'startled'
- A celestial object explodes in the Earth's atmosphere
- November is the hottest in 134 years
- Unexpected surprises about Earth
 Biography of hero Vu A Dinh
Biography of hero Vu A Dinh History of hematology
History of hematology Who is Mr. Tam Da 'Phuc-Loc-Tho' and what does it mean?
Who is Mr. Tam Da 'Phuc-Loc-Tho' and what does it mean? Unbelievable facts about the history of the oil and gas industry: Gasoline used to be cheaper than water, so abundant that it had to be dumped into the river...
Unbelievable facts about the history of the oil and gas industry: Gasoline used to be cheaper than water, so abundant that it had to be dumped into the river...