Principle of operation of the steering system
When driving, you turn the steering wheel, your car will turn to the direction you want. Have you ever wondered why this is so? Find out about the working principle of driving systems on cars to help you drive safer.
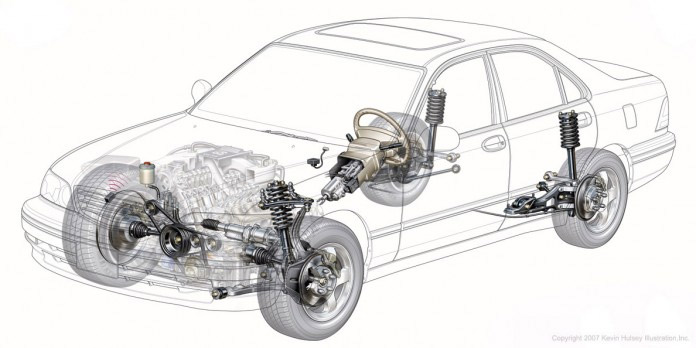
The following will be some of the most basic knowledge about the car's navigation system . We will study the working principle together, some basic navigation systems and its impact on the fuel economy of the vehicle. Let's consider what makes the car divert. Surely it is not as simple as you think!

Figure 1: Diagram of car steering system layout
First of all, you will be surprised when the navigation, the front wheels do not go in the same direction. Why so? In order for the car to turn smoothly, each wheel needs to follow a different circle. Because the inner wheel moves in a circle with a smaller radius, the rotation is more difficult than the outer wheel. If you draw a line perpendicular to each wheel, those lines will intersect at the center of rotation. The geometry diagram below shows that the inner wheel will have to spin more than the outer wheel.
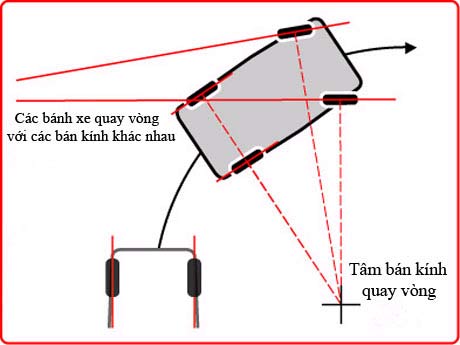
Figure 2: Diagram to simulate turning radius
So far, there have been a couple of different steering mechanisms. The most general summary is the Rack-and-pinion and screw-wheel gear (recirculating ball). First of all, we consider the principle of gear system - tooth bar.
Figure 3: Please click on the steering wheel to see the principle
The gear-bar steering mechanism appears very quickly and is commonly used on passenger cars and small trucks, SUVs. It is a fairly simple mechanical structure. A gear is connected to a metal tube, a tooth bar is attached to a metal tube. A tie rod connects to the ends of the rack.
Round gear is connected to the steering shaft. When you rotate the steering wheel, the rotating gear makes the bar movement. The connecting rod on the two ends of the rack is attached to a lever arm on a spindle (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Steering system with guide wheel in independent suspension system
Pair of gears - rack teeth do two tasks:
- Converting the rotation of the steering wheel rim into the linear motion necessary to change the wheel direction.
- It provides a deceleration, power boost to change the direction of the wheels more easily and accurately.
On most cars today people often have to rotate the steering wheel three to four rounds to redirect the wheel from the left end to the right end and vice versa. The transmission ratio of the steering wheel box is the ratio that indicates the relationship of the steering wheel rotation angle to the angle at which the wheel changes direction. For example, if the steering wheel turns a circle (360 degrees) and the car turns 20 degrees, then the steering ratio is 360 divided by 20 by 18: 1. A high ratio means you need to turn the handlebar. more for the wheel to change direction according to a given distance. However, a high transmission ratio will not be as effective as the low transmission ratio. In general, light and sport cars have lower ratios than larger cars and heavy trucks. The lower ratio will make the steering wheel react faster, you do not need to rotate multiple steering wheels when cornering is folded, and this is a feature that benefits racing cars. These small cars are quite light so just need a low-ratio steering wheel, big vehicles often have to use a higher ratio steering wheel to reduce the driver's impact when driving cornering vehicles.
Some cars have gearboxes with variable ratios, still using gear teeth but have different pitches in the middle and outer parts (pitch is the number of teeth per unit of length). This makes the car react faster when the driver starts driving but reduces the force when the wheels are near the limited position.
Gear drive system - gear bar is supported

Figure 5: Diagram of powered steering system
In this steering system, the bar is designed slightly differently than the usual one. Part of the rack bar contains a cylinder and a piston is always in the middle position. The piston is connected to the rack. There are two liquid pipelines on either side of the piston. A high-pressure fluid (usually hydraulic oil) will be pumped into a pipe end to propel the displacement piston, supporting the shifting rod. Thus, when you drive to any side, there is also the support of the hydraulic system to that side.
The steering-screw-toothed steering gear mechanism
This structure is currently used on most trucks and SUVs. The alignment of the parts in the structure is slightly different from the gear-toothed steering mechanism.

Figure 6: Diagram of layout of details in the steering system
You can imagine that the structure has two parts. The first part is a metal block with an empty thread in it. Outside of this metal block, there are several teeth that match a ring of teeth (can move a lever arm). The handlebar ring is connected to a threaded shaft (like a large ellipse) and fits into the threaded grooves on the metal block thanks to the round balls (see Figure 7). When he turned the steering wheel rim, Ecuador turned. It was supposed that when it turned on the ool, it had to go deep into the metal block in accordance with the thread principle but it was retained so the metal block had to move backwards. This made the gears fit with this metal block and led to the movement of the lever arms making the wheels turn.

Figure 7: Gear-screw-toothed steering mechanism
As shown in the figure, the ui fits into the metal block thanks to the round marbles. These balls have two effects: one is that it reduces friction between parts. Second, it reduces the structure of the structure. Exposure appears when turning the steering wheel, if there are no marbles, the teeth will be separated for a moment causing the steering wheel's dirtiness.
The power system of this steering mechanism is similar to that of the gear-steering mechanism. Support is also carried out by introducing a high-pressure fluid flow on one side of the metal block.
Hydraulic pump

Figure 8: Location of power pump in the steering system
To provide the hydraulic system with support for the steering system, a vane-type hydraulic pump is used (Figure 8). This pump is driven by the torque of the motor by pulley-belt drive. It consists of many vanes (valves) that can move the glass direction in the grooves of a rotor. When the rotor rotates, under the effect of centrifugal force, the blades are thrown out and closed to an oval-shaped space. Hydraulic oil is pulled from the pipe with low pressure and compressed to a high pressure output. The amount of oil supplied depends on the speed of the engine. The pump is always designed to provide enough oil as soon as the engine is idling, and thus it will provide too much oil when the engine is operating at high speed. To avoid overloading the system at high pressure, a pressure relief valve system must be installed (see Figure 9).

Figure 9: Structure of the vane-type power pump
The power steering system will assist the driver when he exerts a force on the steering wheel rim (when he wants to divert the car). When the driver does not exert any force (when the vehicle is moving straight), the system does not provide any assistance. The device used to sense the force acting on the steering wheel ring is called the rotary valve .

Figure 10: Rotary valve structure diagram
The main detail of the rotary valve is a torsion bar . The twist bar is a thin metal rod that can be twisted when a torque is applied to it. The top end of the torsion bar connects to the handle ring and the lower end connects to the gear or screw, so the entire torque of the torsion bar is balanced with the total torque used by the driver to change the wheel. The larger the torque that the driver operates, the more the twist of the bar.
Figure 11: This animation will tell you the operation of the rotating valve and the closing, opening the valves when you apply the force to the steering wheel (please click on the center of the white circle to see the working principle of Rotary valve)
The input of the steering wheel shaft is an internal component of a cylinder cylindrical valve block. It also connects to the upper end of the twist bar. The bottom of the twist bar connects to the outside of the pipe valve. The twist bar also rotates the output of the steering mechanism, connecting to the gear or screw depending on the type of steering system.
When the twist bar is twisted, it causes the inside of the rotating valve to be relative to the outside. Since the inner part of the pipe valve is also connected to the steering wheel shaft (ie connected to the steering wheel rim), the total angle of rotation between the inside and outside of the pipe valve depends on the driver turning the handlebar.
When the steering wheel has no impact, both hydraulic pipes provide the same pressure for the steering mechanism. But if the pipe valve is turned to one side, the pipes will be opened to provide high-voltage flow to the pipe on that side. However, these auxiliary systems have low efficiency. We study some future systems for higher performance.
Electric Power Steering System (Electric Power Steering)
 Electric power steering system
Electric power steering system
1. Steering wheel (hand steering force); 2. Electric servo motor; 3. Reaction from road surface to tires; 1 + 2. Power when driving
The operating principle of the electric power steering system is based on the signal of the torque sensor located in the power steering. When the driver acts on the steering wheel, it is necessary to change the direction, under the effect of the reaction from the road surface through the wheel, the steering wheel acts on the torsion bar located in the electric power assembly. The torque sensor works to measure the driving torque (the deformation of the torsion bar) from which to send the signal to the control box. Based on the signal of the torque sensor, the control box gives the motor drive power line large enough to support the steering wheel rotation in the direction of the driver, so the driving force will be supported. and become much lighter.
Compare electric power steering and hydraulic power steering systems
When comparing electric power steering system with hydraulic power steering system, the electric drive system has many outstanding advantages compared to hydraulic steering system, specifically:
- The electric drive system does not need to drive from the engine so the engine does not have to use hybrid power for the power steering system so it will save 2% -3% of fuel when operating.
- The electric drive system does not use the fluid (hydraulic oil) to drive power, so it ensures more environmental hygiene .
- Electric steering system has a simple structure, much lighter than hydraulic steering (weight reduction -> fuel saving).
- The electric steering system gives a more realistic driving feel at high speeds.For hydraulic steering, the higher the speed, the lighter the driver makes the driver more susceptible to driving and the vehicle is unstable especially when cornering is urgent.For electrical systems, this is completely different, lightweight support when low speed and heavier when the car runs at high speed, this gives a more realistic, more solid driving feel.
- Electric steering power is lighter and more sensitive than hydraulic power steering.
Although there are many advantages, the biggest disadvantage of power steering system is repair cost . When the details inside the powerhouse are broken, it is necessary to replace the entire power steering unit without repairing it to ensure safety when driving, without losing the driver suddenly.
Driving system on cars
- Steer-by-wire electronic steering system
- American self-propelled rams hit the divider because they did not see the road
- Operation principle of safety belt
- Operation principle of automatic transmission
- Ferrari patented steering system more accurate
- The principle of operation of the differential
- The operating principles of car brakes
- Steering wheel driver instructs drivers when they are dazzled
- Principle of operation of car ignition system
- Smart steering wheel detects sleepy driver
- Principle of operation of air coolers
- The steering wheel detects driving drowsiness
 'Barefoot engineer' invents a pipeless pump
'Barefoot engineer' invents a pipeless pump Process of handling dead pigs due to disease
Process of handling dead pigs due to disease Radiometer
Radiometer Warp Engine: Technology brings us closer to the speed of light
Warp Engine: Technology brings us closer to the speed of light