The age of the universe is about 13.8 billion years but why can we observe 93 billion light years?
Is there something wrong with the big bang theory, or is the theory of relativity itself wrong?
Age and size of the universe
Before starting our journey to discover the mysteries of the universe, we need to understand the age and size of the universe. This is the basis for understanding the expansion of the universe and phenomena faster than the speed of light. The age of the universe is estimated by observing the cosmic microwave background radiation.
Microwave background radiation is left over from the Big Bang and permeates every corner of the universe. By analyzing subtle temperature fluctuations in the microwave background radiation, scientists can trace the history of the universe and estimate that it is 13.8 billion years old. However, the size of the universe exceeds our intuition. As the universe continues to expand, space itself continues to expand, allowing light to travel greater distances over the universe's history than its actual age.
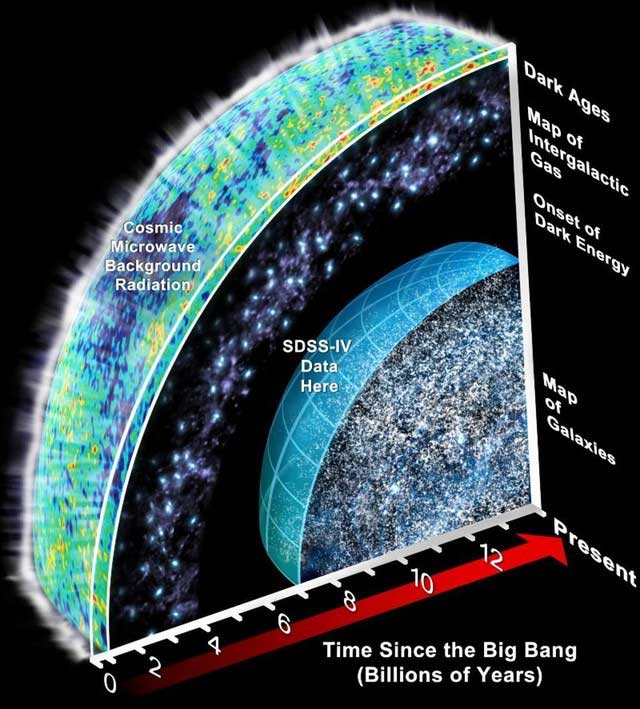
The age of the universe is estimated by observing the cosmic microwave background radiation. (Illustration).
Therefore, even though the universe is 13.8 billion years old, the diameter of the universe that we observe still reaches a staggering 93 billion light years. One of the direct evidences of the expansion of the universe is Hubble's law, which reveals a simple but profound truth: the farther galaxies are from us, the faster they will move away . This regression rate can be measured by observing the redshift phenomenon.
Redshift refers to the phenomenon in which the wavelength of an object's electromagnetic radiation increases for some reason. It is a direct result of the expansion of the universe. In addition to redshift, scientists also observe the expansion of the universe through other methods, such as detailed observations of distant galaxies that have revealed how the expansion rate of the universe changes as how over time. These observations not only help scientists build more accurate models of the universe, but also introduce concepts about dark matter and dark energy, invisible but important components of the universe.

The farther galaxies are from us, the faster they will move away. (Illustration).
Relativity and the expansion of the universe
Einstein's theory of relativity is one of the foundations of modern physics. It consists of two parts: special relativity and general relativity. Special relativity proposes the concept of the speed of light as a constant speed, while general relativity considers gravity as a curvature of space-time caused by matter.
One of the most famous conclusions of the theory of relativity is that no object with rest mass can reach or exceed the speed of light. This is because when the speed reaches the speed of light, the mass of the object would need to become infinite, and the energy it would need would also be infinite to accelerate.
However , the expansion of the universe does not involve the movement of matter in space but the expansion of space itself. This means that galaxies are not moving through space faster than the speed of light but are being swept along by the expansion of space. Therefore, the expansion of the universe does not violate the limit of the speed of light in the theory of relativity.
To make it easier to understand, let's use an analogy to draw some points at a certain distance with a marker on an uninflated balloon, these points represent galaxies in the universe. When the balloon is not inflated, all the points are relatively close to each other. But as you start to inflate the balloon, you'll notice the distance between the points start to increase.

As the balloon expands, the points on the surface will increase their distance from each other. (Illustration).
Note that the points themselves do not move; Their relative positions remain the same. In this model, the surface of the ball represents a two-dimensional space similar to a three-dimensional space. As the balloon expands, the points on the surface will increase their distance from each other. This is not due to points moving on the surface but the entire surface expanding. Of course, this model is a simple metaphor. The universe is not two-dimensional but three-dimensional, and its expansion may be more complex than the surface of a balloon. But this model provides an intuitive way to understand the basic concept of the expansion of the universe. In the balloon model, if the balloon expands infinitely, the distance between points will increase at an infinite rate . In the real universe, due to the expansion of space, the distance between galaxies can increase faster than the speed of light, and this does not violate the principle of relativity, because the theory of relativity "does not allow" matter. exceeds the speed of light, but space does not.

In the universe, the distance between galaxies can increase faster than the speed of light, this does not violate the principle of relativity. (Illustration).
The deeper meaning of the expansion of the universe
The expansion of the universe is not only an observable phenomenon, it also challenges our laws of physics and requires us to rethink the nature of mass, energy, time and space. space. As space can expand indefinitely, the important question is whether our laws of physics need to adapt to this infinite framework.
Research into the expansion of the universe also led to the concepts of dark matter and dark energy. These are forms of matter and energy that we cannot observe directly, but through their influence on the expansion of the universe, we know that they make up the majority of the total energy in the universe.
Dark matter influences the rotation speed of galaxies and the motion of galaxy clusters through gravitational effects, while dark energy is the mysterious force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe. How they interact with the expansion of the universe and what their nature is is one of the most exciting areas of research in modern physics. The expansion of the universe also poses challenges to our future observations and theories.

Dark matter affects the rotation speed of galaxies. (Illustration).
As the universe continues to expand, distant galaxies will get farther and farther away from us and may eventually go beyond our range of observation. This means we may be losing our window into the early history of the universe, while also limiting our understanding of its ultimate fate. Although the expansion of the universe is widely accepted as a fundamental fact of cosmology, the exact mechanism behind it remains largely unknown.
- The mysterious circle is the largest 5 billion light-years from the universe
- The universe may be 'younger' than 2 billion years old
- Scientists measure the total amount of light produced in the universe
- Discover the oldest disk galaxy
- As early as 2.8 billion years the new universe dies, don't be too afraid
- Light from the first stars
- Capture the most distant object in the universe
- The frame of the universe
- The largest structure in the universe contains just 1,600 galaxies
- Discover the oldest galaxy in the universe
- Discover the largest
- Things you don't know about the speed of light
 'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times
'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why?
The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why? History of the iron
History of the iron What is alum?
What is alum?