The mystery behind launching deadly bacteria into space
SpaceX is preparing to launch an important project. They are about to launch a deadly super bacterium, capable of resisting antibiotics into orbit on February 18 . This bacterium will exist in the zero gravity environment of the International Space Station (ISS).
This idea is not to "weaponize" space with MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). MRSA is a bacterium that kills more Americans each year than HIV / AIDS, Parkinson's disease, emphysema (permanent and irreversible destruction in the walls of the air chambers of the lungs, and called alveoli), and killing people together. Bacterial transmission into orbit helps scientists probe pathogens before they appear on Earth.
SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket used to launch MRSA into space is a research funded by NASA. MRSA will be "cultivated" at the US National Laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
"We will take advantage of the zero gravity environment on ISS to promote the medical revolution, just like the revolutions on Earth," said lead researcher Anita Goel, and chief executive officer of public affairs. Nanobiosym Biotechnology Company, speaking on Yahoo News.
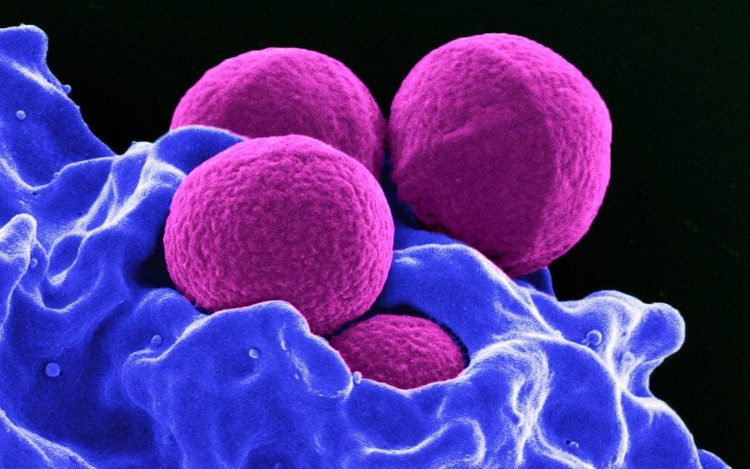
MRSA bacteria are a major threat to humans.(Photo: NIAID).
In 2015, Nanobiosym developed a device called RADAR gene . This is the world's first mobile scanner , enabling real-time diagnostics of any disease. However, patients with this device only cost one tenth of the cost compared to similar test machines.
The device will be used on the International Space Station, to assess the mutation level of two MRSA strains when they react to a zero gravity environment.
Since then, Goel and his team will develop models that predict germs that can resist antibiotics. These pathogens are capable of causing changes on Earth in the coming years. The study will help drug makers have the opportunity to pre-screen bacterial resistance mechanisms.
"The ability to predict mutation levels of Gene-RADAR will lead to the emergence of new generation antibiotics. They will be built more effectively to prevent the spread of the world's most dangerous pathogens. " Goel said.
At this stage, the team is not sure how MRSA will react to their new home in Earth orbit. But previous studies of space bacteria have shown that the environment can lead to growth, mutation, and increase the number of bacteria at a rapid rate.
This is because in space, some metabolic proteins become more active. Low-dose space radiation may also alter the activity of certain genes.
A 2000 experiment proved this. After 40 days on the Mir (Russian space station operating in low Earth's low orbit from 1986-2001), the rate of mutation in a bacterial gene was added to yeast, three times higher. times compared to when they were on Earth.
Another study in 1999 showed that some E. coli strains had higher mutation frequencies after a space trip. But the type and frequency of mutations are very different. They depend on the living conditions of E. coli strains in space.
From the incredible results clearly shown in NASA studies, we see there are still many mysterious things about space. Special is how space confuses us both in good and bad terms.

Studying MRSA bacteria in space is a job to be done as soon as possible.
But many scientists believe that the effect of gravity is the main cause of the mutation of bacteria. They also suspect that exposure to radiation outside the protective barrier of the Earth's magnetic field is also influential.
"Many researchers have agreed on: the weightless environment has a great influence on the growth and behavior of bacteria. Radiation can increase the mutation rate of microorganisms during flight. " a researcher said. If the Goel hunch is correct, and the space actually makes the MRSA mutant, it's like we can observe all the steps of the opponent, like playing a game of chess.
Currently, the scientific community does not need to wait too long to develop new drugs to help people treat effectively. They can quickly look at the growth of MRSA bacteria in space, and produce new antibiotics for centuries.
This is a very important thing, because antibiotics are something that researchers are extremely interested in. Because bacterial diseases are one of the biggest threats to humanity. They threaten to kill hundreds of millions of people worldwide in the coming years.
With 90,000 Americans infected with MRSA, and 20,000 die from it each year, studying MRSA bacteria in space is a task to be done as soon as possible.
- Close up of beautiful deadly bacteria surprised
- Deadly bacteria attack Europe again?
- What kind of bacteria can kill hundreds of millions of people coming out from the North Pole?
- The 800-year-old skeleton contains 'ghost cells' of deadly bacteria
- Discover shock about bacterial growth in space
- New mode of spread of deadly bacteria in food
- Improper washing of chicken can spread deadly bacteria
- Israel announces plans to experiment with bacteria in space
- Russian space exploitation and use
- Detecting lethal and deadly pathogenic bacteria in South America
- The deadly bacteria in this day can explode when antibiotic resistance comes
- Testing to bring the metal mining bacteria to the International Space Station
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people