The origin of the term El nino
The term El nino (Spanish means "comedic Lord" or "little boy") was started to be used by fishermen along the coast of Ecuador and Peru to indicate a phenomenon of warm currents occurring. around Christmas and lasts about a few months. During this time, fish are less, so fishermen often stay at home to repair fishing gear. In some El nino cycles, this warm current phenomenon interrupts the fishing season until May or June next year. Over the years, the term El nino is used to refer to the phenomenon of warm currents and its effects not only for fishermen in Ecuador, Peru but also for different industries around the world. .
What is El nino?
According to the simplest definition, El nino is a phenomenon that breaks down the normal conditions of the ocean-atmosphere system in the tropical Pacific region, causing global weather impacts.
Or according to a different definition El nino is a phenomenon of tropical waters in the tropical Pacific warming abnormally.
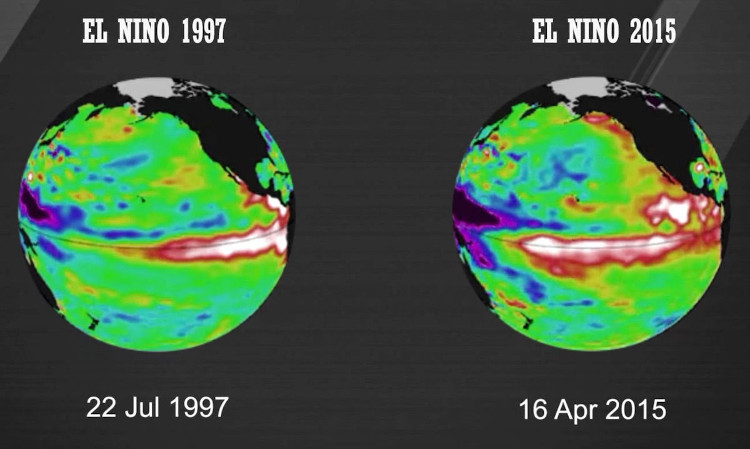
El nino is a phenomenon that breaks down the normal conditions of the ocean system.
What is La nina?
La nina in Spanish means "little girl", right from this name we can understand L a nina as an inverse phenomenon of El nino. La nina is a phenomenon in the tropical region of the Pacific Ocean which is unusually cold.
La nina is also known as El Viejo or Anti - El nino.
What causes El nino?
El nino is the result of the interaction of the sea surface in the tropical Pacific region with the atmosphere just above it. This is a phenomenon caused by the internal force between the two ocean poles - the atmosphere. The width of the Pacific Ocean is also one of the causes of the El nino phenomenon. External interactions such as volcanic activity (on land or in the ocean), sunspot cycles are not related to the El nino phenomenon.
To better understand the phenomenon of El nino and La nina, let us consider the developments in the Pacific tropical region under normal conditions and when these phenomena occur.
In the normal trade-wind condition, it blows from East to West and puts hot water back in the Western Pacific. Therefore, the sea level in Indonesia is about 0.5 m higher than the sea level in Ecuador. Sea surface temperature in the West is about 8oC higher in the East. In South America the interface between the warm water layer above and the cold water layer below is not very deep, enabling cold water from below the surface water to float to the surface. This cold water contains many nutrients, promotes the development of primary production organisms, making the marine ecosystem more diverse and the fish catches increase. During this period, the increase in the warm sea area (Western Pacific) and decrease in the Eastern Pacific region.
When the El nino phenomenon, trade winds weakened in the central and Eastern Pacific regions. Hot water flows from the western Pacific coast to the East Pacific coast. This process causes the surface of the hot water layer above and the lower cold water layer to descend further, thus inhibiting the rise of the cold water layer, making the eastern region less productive creatures and fish. The momentum also increased in the direction of the flow of hot water causing floods in Peru and drought in Indonesia and Australia.
El nino cycle
El nino usually occurs irregularly, but lies within a period of 2-7 years. Each episode of El niđo has different intensity and amplitude of time.
The following is a forecast map of La nina's impact on global climate.

The impact of La nina on global climate.
Translation: Le Hoang Viet
- El Nino 2015 looks strange with the peak of 1997
- Haze in northern Thailand: due to the influence of El Nino?
- El Nino changes may cause many storms to land
- Nature is angry, El Nino will be more intense
- Can 2015 El Nino cause more natural disasters?
- El Nino can last until May 2010
- El Nino is coming back
- El Nino is about to end in the Caribbean
- El Nino may stop working in the middle of this year
- There is no link between El Nino and climate change
- El Nino is back
- El Nino is getting worse due to rising temperatures
 Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity?
Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity? Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer
Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer Lightning stone - the mysterious guest
Lightning stone - the mysterious guest Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance
Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance