What is endometriosis? Is it dangerous?
If the woman has frequent abdominal pain during menstruation, she may think about the possibility of endometriosis. This is a benign disease but causes many discomfort and pain for patients every time they are menstruating. Moreover, the disease also poses a risk of infertility in women.
What is endometriosis?
The endometrium is the lining of the uterus, located on the uterine surface and separated from the uterine muscle layer. This mucosa is affected by estrogen activity during a woman's menstrual cycle. Every menstrual period, because the process of conception does not take place, the endothelium will peel off and float away with the blood. But for various reasons, these endothelial debris flows back into the fallopian tube or up to the ovary. When these mucosa outside the uterus are called endometriosis. When blocked in the ectopic parts, the debris will cling to the area and begin to grow, causing inflammation and bleeding. In some cases, endothelial debris can penetrate further areas in the abdominal cavity such as the area around the intestine or bladder.
This condition is more common in women of reproductive age and less common in menopausal women. The age at highest risk for this disease is in the range of 30-40 years, but the disease can occur in girls from 8 years old and older. According to US statistics, an average of 6-10% of women suffer from endometriosis. In the UK, 1 in 10 women of reproductive age are experiencing this condition.
The cause of endometriosis
The exact cause of this situation has not been determined yet, but some agents are mentioned. Many assumptions, such as the mechanism of menstrual reflux, congenital, proliferation of uterine endothelial cells . have not been clearly demonstrated.
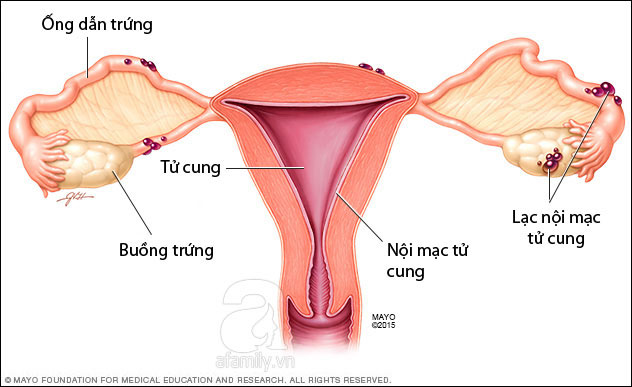
Endometriosis is common in women of reproductive age and is less common in menopausal women.
- During menstruation, some blood may flow back into the fallopian tube and into the abdomen. The immune system in some women reacts and produces immune responses. Normally, when menstruation, the uterus has slight contractions from the body to the cervix to push the blood vessels and the uterine mucosa to the outside, but in some people there are inversions when menstruation should pushes the blood vessels upwards and the blood vessels spill into the ovaries and abdomen. In this menstrual cycle, there are endometrial cells that are "fresh", which means that when they "peel" around the abdomen, they stop and develop and suffer from estrogenic effects every month, so they get bigger. But unlike when these cells in the uterus are peeled off and expelled, they make cocoons in the abdomen that do not peel off but become bigger and bigger. The more mucosal lining of the abdomen is, the more endometriosis is created.
- Problems with the thyroid gland also increase the risk of endometriosis.
- Genetic factors also affect the ability of endometriosis. Science has proven that a mother has endometriosis, girls are also likely to suffer.
- Another possibility is that during embryonic development, endometrial cells may fall out of the uterus and to surrounding organs.
- Endometriosis is also affected by environmental factors but the exact mechanism is still unknown to everyone.
- There is a theory that there are cells in the body that suddenly develop one day and turn into endometriosis, or due to the legacy of the primitive cells of the uterus at birth. .
- When cesarean section (common) or interfering with the uterus (gynecological intervention) makes the uterine lining fall into the abdomen that causes endometriosis.
Some other causes may be because your immune system has a problem that makes it impossible for the body to recognize and destroy growing endometrial tissue outside the uterus, causing endometriosis. Moreover, you can get sick when the abdominal and pelvic cells can be transformed into endometrial cell walls, or already formed endometrial cells outside the uterus when you are still present. is the fetus.
Endometriosis often involves the entire oviduct, ovary, intestine or tissues in the pelvic floor. Surrounding endothelial tissue can be irritating and painful, forming scar tissue and fluid-containing sacs that make it difficult to get pregnant.
Common symptoms
The main symptoms of the disease are pelvic, lower back and lower abdomen pain. These pain can get worse every menstrual period or when having sex. In addition, symptoms such as intestinal pain, flatulence and nausea during pain or digestive problems (diarrhea, constipation, indigestion .) when menstruation is also common signs of the disease .
Another typical symptom of endometriosis is menstrual disorders such as pain, prolonged cycles and heavy bleeding. If you find your menstrual cycle is unstable, the amount of menstrual irregularity requires visiting your doctor. Many women do not even detect the disease until they are found to be infertile.
Some common signs and symptoms of the disease include:
- There are pelvic pain during menstruation and pain is getting worse with time;
- Lumbar pain and abdominal pain;
- Pain during or after sex;
- Pain during defecation, urination during menstruation;
- The time of your menstrual period may be longer or more bleeding;
- Blood in the stool or urine, vaginal bleeding after sex;
- Fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence or nausea, especially during menstrual periods;
- Pain in the menstrual period;
- Pain before and during menstruation;
- Infertility;
- Tired;
- Meet some gastrointestinal disorders such as diarrhea, constipation, nausea.
Can endometriosis become pregnant?
Endometriosis causes an inflammatory condition that adheres to the urinary tract, the two uterus are twisted or inflamed causing sclerosis, which causes the movement to be restricted or lost, unable to catch the ovule when released from the chamber eggs (or ovulation).
When endometriosis in the ovary will destroy the organization of the ovary, naturally destroy the follicle follicles or due to inflammation and stick with thick ovaries to prevent ovulation. When the uterine endometrium is in the uterine wall, it will make the soft soft uterus affect the movement of the sperm or ovule, even if it will prevent or block the uterus that causes the uterus to cause infertility. When the endometrium in the uterine wall changes the environment of the uterus, the embryo (if the fertilized ovule) dies. A lot of inflammation in the abdomen limits or prevents the mobility of the uterus.
Several factors can lead to infertility due to endometriosis:
- Fallopian tubes are very small and very easily blocked. Any obstacle that interferes with eggs along the fallopian tubes can cause infertility.
- The surrounding spots can prevent the egg from moving along the fallopian tube, preventing the sperm from reaching the egg.
- Sticks can move the positions of ovaries and ovaries in the pelvic area.
- The lost endometrium can cover the entire ovary, preventing the egg from falling into the fallopian tube.
- When the endometrium appears in the uterus will cause bleeding. Similarly, when it is on the ovary, menstruation will appear. If there is no way to remove it, the old blood can form pockets containing blood on the ovary and affect ovulation.
- The substances secreted by pelvic infections can all be detrimental to the sperm as well as preventing the egg from entering the uterus. There are also times when these substances affect the endometrial cells themselves, leading to some problems during conception and early development of the embryo.
- In some people, ovulation may be interrupted. If the number of eggs is low and ovulation is abnormal, the chances of conception will decrease.
- Endometriosis will reduce egg quality as well as fertility and ability to grow.
Only about one third of women with endometriosis are having difficulty conceiving. In fact, only when large and sticky scars affect fertility. Therefore, there are also many women who suffer from endometriosis and are still pregnant normally. Some people are diagnosed after having children. Even so, endometriosis is still one of the leading causes of infertility for women. Although some women may be pregnant, the results are not high because the development of endometriosis blocks is often directly proportional to the time at which pregnancy is inversely proportional to time. If the endometrial mass is small and small (mild level), the rate of pregnancy is high, and the mass is large, large, the abdomen is more likely to become pregnant.
How to treat and prevent endometriosis
Currently, there is no thorough treatment for this disease. Current treatments are designed only to relieve the pain of the patient and reduce the development of endometriosis. Often, people who are sick will be prescribed painkillers or hormonal balancing drugs, but these drugs cannot be treated completely and will be ineffective when stopped. At the same time, you will likely face many harmful side effects such as early menopause, vaginal dryness, decreased bone density, leading to an increased risk of osteoporosis. In the most severe case, you may have to undergo laparoscopic surgery or hysterectomy.
If you cannot tolerate the pain, you only need to take hormone therapy to reduce the amount of estrogen in your body to make the tissue sample shrink. However, if you are planning to become pregnant, you can simultaneously treat infertility and surgery.
If you have only mild pain, don't plan to become pregnant or are close to menopause, you may not need treatment. Drugs that include contraception can be used to prevent progression of endometriosis, or anti-inflammatory drugs, to help you manage pain. When your pain becomes more intense or if the above drugs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs do not work, you should try a stronger hormone therapy.
If strong hormone therapy still has no effect or other organs are affected, then the next step is surgery. Large endometrial blocks and scar tissue will be removed during surgery. These surgeries will be one or more endoscopic surgeries, taking the endometrial cells while helping to remove the surrounding organs, bringing them back to their normal positions. However, surgery is not always effective, especially in severe cases. Some studies show that surgery even reduces the chances of getting pregnant more.
When removing the blood bags on the ovary, the ovarian tissue may be mistakenly taken. In addition to affecting the ability to ovulate later, it also leads to the risk of early menopause. The removal of endothelial cells is always risky and requires high experience and accuracy. Any surgery has complications but many people still take risks to have children and reduce pain.
A common treatment is to use drugs to stop ovulation . You can use oral contraceptives or combination hormones containing progesterone.
Some people already have enough babies and life is heavily disturbed by endometriosis, they may choose to have a hysterectomy. This is the final solution and should be carefully mentioned when the symptoms too affect daily activities.
Measures to prevent endometriosis
- Regularly monitor your menstrual cycle : Pay attention to the stability of time, menstrual blood flow as well as pain before and during menstruation. If the menstrual cycle is abnormal, you need to see a doctor for a visit.
- Daily cleaning of the private area to keep this area clean and dry. You should also take care not to exert a deep impact on the inside of the vagina to avoid the bacteria from getting inside that can cause inflammation.
- Always keep a healthy lifestyle, exercise regularly , especially to avoid obesity. You should also stay away from alcohol and stimulants like caffeine. These measures help maintain the balance of estrogen - a hormone that stimulates the growth of endometrial cells.
- 10 most dangerous animals on the planet
- Video: Dangerous germs hidden in Arctic ice are melting
- The most dangerous shark assassins in the ocean
- In the plethora of deadly epidemics, what is the most dangerous virus in history?
- Dangerous behavior of adolescents
- 20 world's most dangerous creatures lethal in a split second (part 1)
- The US removed the ban on fundraising for research on
- Learn some dangerous blood diseases
- Young people often get caught up in dangerous games
- The most dangerous storms in Vietnam
- Six most dangerous dishes in the world
- Crocodile is more dangerous than a shark 168 times
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking