Winter and bronchopneumonia in children
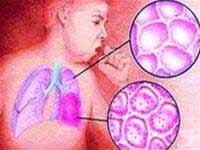 Bronchitis - pulmonary inflammation is an acute inflammation of the small bronchus, alveoli and organization around the alveoli. Often inflammation spreads both lungs, it is very serious and causes respiratory failure. The disease is common in winter, progressing badly, easily leading to death.
Bronchitis - pulmonary inflammation is an acute inflammation of the small bronchus, alveoli and organization around the alveoli. Often inflammation spreads both lungs, it is very serious and causes respiratory failure. The disease is common in winter, progressing badly, easily leading to death.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), acute respiratory infections account for 50% of all diseases in children under 5 years old and 30% in children aged 5-12 years. Mortality rate 75% in acute respiratory infections.
According to WHO, the total number of deaths per year in children under 5 years old worldwide for all causes is 13 million, of which pneumonia accounts for 30% (4.3 million). In Vietnam, a child may have acute respiratory infections 3-5 times / year (ie 8-10 million times a child), which is the leading cause of death in respiratory diseases.
Reason
Due to Hemophilus influenzae and then staphylococci, streptococci, parasites, fungi and influenza viruses.
Advantageous factor
- The climate is cold, the weather changes in the winter-spring months.
- Young children, premature babies, malnourished children.
- Bronchitis is also seen in frail elderly people and immunocompromised people.
Causes: environmental pollution, damp houses, cigarette smoke. Allergic sites or children with measles, flu, and whooping cough.
Symptoms of bronchitis - lung:
- Children often have a high fever of 38-39o.
- The elderly and malnourished children sometimes have no fever.
- Patients often tired, fussy, dry lips, little sucking or sucking.
- At first, a dry cough, after a lot of phlegm, children who do not know sputum often swallow.
- Difficulty in shortness of breath, shallow breathing over 50 times / minute; The nostrils of the nose are bulging, the chest is retracted, the lips and head of the limb are cyanosis, when the disease is severe, the breathing rhythm can be disturbed.
- Listening to the lungs with moist, ranny, snoring ridge scattered in one or both lungs.
- X-ray has blurred notes scattered in two lungs.
- High blood count and polymorphonuclear leukocyte count.
Management when suffering from bronchitis - lung
If detected and treated early, the disease will recede. Often bronchitis - lung disease is very severe, late treatment can lead to death. When suffering from bronchitis - lung in children or the elderly should be monitored in medical facilities. If severe, it should be taken to hospital and treated with the following measures:
- Anti-bacterial infection with antibiotics such as penicillin, erythromycin, methixilin, cefalosporin II, III, quinolone group . Combining two or three antibiotics when needed.
- Difficulty breathing, respiratory failure, give oxygen.
- Treatment of cardiovascular electrolyte disorders, vomiting, if any.
- Comprehensive care: warm up, eat milk, drink enough water daily. Reduce cough by taking traditional medicine such as steamed rose with sugar candy or decoction of leafy leaves also called radiant tree. If high fever use antipyretic drugs such as paracetamol.
Prevention
- Breastfeed, eat enough food to improve your condition.
- Keeping the environment clean, hygienic in kindergartens, schools, maternity homes. Vaccinations expand prevention for children according to regulations.
- No smoking in a bedroom with children, in nursery.
- If measles and pertussis outbreaks are detected, especially in the current period of bird flu, they must be isolated in time to avoid spreading to other children, because these diseases are one of the causes of inflammatory complications bronchus - lungs.
- 4 things to avoid when bathing children in winter
- Children born in the Winter - Spring season know more cows
- Keep babies warm in the winter
- Winter-born babies are insane?
- 10 principles for not getting sick in the winter
- Do not take a lot of bathing in the winter to avoid itching
- Hanoi winter moments
- Winter this year comes early, colder than the last 5 years
- The disease is common in the winter
- Please admire the poetic beauty of Hanoi winter
- Children often encounter Winter-Spring season and preventive methods
- Children and the risk of autism
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking