7 harmful effects of antibiotic abuse
In addition, the downside of the "antibiotic era" began to emerge , people have to pay for abuse, drug resistance and many other dangers that people have not yet fully estimated.
"Harmful" beneficial bacteria
One of the downside of long-term antibiotic abuse is friendly bacteria. In fact, antibiotics have a broad spectrum that destroys both good and bad bacteria. So if used improperly, abuse will kill the beneficial bacteria in the intestinal tract, imbalance bring the natural nature of the body. Once unbalanced, bad bacteria rage, easily develop many incurable diseases, such as stomach disorders, make diseases more serious and reduce the effectiveness of antibiotics.
Probiotics can be added, especially after a period of antibiotic use. Refer to your doctor about probiotics for proper use, including those with fibroids, bacteria that have penetrated parts of the body.
Increased risk of intestinal autoimmune disease
Autoimmune disease occurs once the body's immune system fails to function properly. Abuse of long-term antibiotics can disrupt this balance, affect the immune system and once damaged, can lead to autoimmune disorders or a chronic disease or infection.
Autoimmune disease is a group of diseases in which the body's immune system targets the wrong target, in other words attacking the body itself. Until now, science has yet to understand the sector's topology, but changing the body's equilibrium is the cause of the disease. According to a 2006 study, changes in intestinal tissue (especially increased permeability due to intestinal bacterial imbalance) were the cause of increased autoimmune diseases, such as Crohn's disease (inflammatory bowel disease). and Celiac disease (fatty stools) .
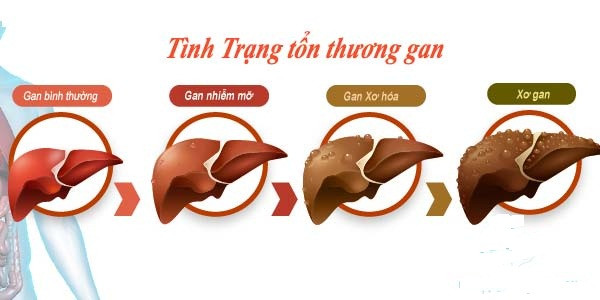
Abuse of antibiotics easily causes liver damage.
Increased asthma and allergies
Asthma is a life-threatening disease that is not managed and treated in a timely and appropriate manner, especially when exposed to too many stimulants. According to a study published in 2009, the use of antibiotics, especially in the early stages, increases the risk of asthma, conjunctivitis (rhinoconjunctivitis) and eczema in school-age children. For this reason, parents should be careful when using antibiotics, so as not to affect the health of their children in the future.
Causes liver damage
Groups of people with strong antibiotic prescriptions often have to go through liver function tests to have a prescription basis. This shows that antibiotics are "engraved" for the liver. Many studies show that antibiotics are very harmful to liver tissue, making liver function test indicators such as AST and ALT soar. Azithromycin, an antibiotic commonly used, is also very likely to cause liver damage. Two weeks after antibiotic treatment should do liver function tests, will see abnormalities related to liver health.
Increased risk of cancer
According to research by Finnish scientists, after comparing data of long-term antibiotic users with cancer patients, many uncertainties have been found. For example, long-term use of antibiotics increases the risk of prostate cancer, breast, lung, colon, ovarian, endocrine, skin, thyroid, and kidney cancers are 1.5 times higher. compared with the non-antibiotic group, both men and women.
Weight gain
According to studies conducted and published in 2014 and 2015, science found that antibiotic use was associated with weight gain in newborns and toddlers. Before these studies, many people believed that antibiotic use was not related to weight gain or excess weight, but the main cause was an unbalanced diet and lack of exercise. With the above findings, when using any medicine for young children, parents should pay attention, consult the doctor carefully, avoid abuse, especially antibiotics.
Create "super" bacteria
Using arbitrary antibiotics, especially arbitrary use, not following a doctor's prescription can " turn " into "painting" , creating a drug-resistant bacterium. When bacteria are constantly exposed to a certain drug, it becomes greasy, like an increase in MRSA bacteria (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus) , does the bacteria cause " staph" infection treatment response when using common antibiotics. Or MDR TB (multidrug-resistant tuberculosis) and recently discovered the presence of malaria parasite strains in Southeast Asia drug resistance.
Alternatives to antibiotics
While science does not understand the cause of antibiotic resistance as well as the evolution of bacteria, the medical community recommends that people use herbs instead .
For example, garlic is both food and spice is equally effective as antibiotics, especially in the case of bacterial food poisoning. Or use some herbal antibiotics instead of ibuprofen, such as high dry white willow bark (white willow bark), cat nails (cats claw - herbs in tropical South America), Boswellia (resistant herbs) Inflammation, prepared from the resin part of the boswellia tree, native plant in India, this aromatic plant resin is thought to prevent leukotrienes, chemicals that damage healthy joint cells, capsaicin (fruit extract) dried ripe of some chili species), curcumin (the main component of curcuminoite, found in turmeric) and aromatic oils .
- Find a mechanism to help bacteria not only resist but also antibiotics
- The CDC report states: The United States has entered a post-antibiotic period
- Cinnamon will save disaster
- 10 million deaths are one of the startling numbers about 'Antibiotic resistance'.
- Bad habits of parents hurt the liver and kidneys, endanger children
- Abuse of vitamin E may reduce life expectancy
- Published 9 pictures illustrating the harmful effects of tobacco
- Natural ways to limit the harmful effects of alcohol
- Supplementing vitamins to reduce the harmful effects of radiation
- The incalculable harm of fireworks
- The danger that people still misunderstand can kill 10 million people every year
- Discover more cases of antibiotic-resistant viruses in the United States
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking