American scientists say the world's first living robot can reproduce
US scientists have created the first living robots, called xenobots, that can reproduce in a way never before seen in animals and plants with the help of artificial intelligence (AI) technology. The study was published in the scientific journal PNAS .

Xenobots were formed from stem cells of the African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis). So, it was named after this frog. Xenobots, which are less than 1 mm (about 0.04 inches) wide, were first discovered in 2020 after experiments showed they can move, work in groups, and heal themselves (self-heal). ).
The world's first reproducible robot was developed by a team of scientists at the University of Vermont, Tufts University and Harvard University's Institute of Bioinspiration Engineering. They say they have discovered a completely new form of reproduction, different from any other animal or plant known to science before.
Biology Professor Michael Levin, Director of the Allen Discovery Center at Tufts University and co-author of the new study, said: 'I was absolutely amazed by it. The way frogs reproduce is very special. They free the cells from the rest of the embryo, thereby figuring out how to replicate in the new environment' .
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that have the ability to develop into different cell types. To create xenobots, the researchers took living stem cells from frog embryos and incubated them. In addition, they do not interfere with any gene-related processes.
Professor Josh Bongard from the University of Vermont, who was part of the research team, said: 'Most of us think that robots are made of metal, steel, ceramics. However, what matters is not where they are made, but what we can do to replace humans. We created a robot that has the full characteristics of the organism and is made from unmodified frog cells' .
Professor Bongard said they discovered xenobots, which are originally spherical and made of about 3,000 cells and can regenerate. The xenobots used a mechanism of 'kinetic replication' , a process that occurs at the molecular level but has never been observed at the scale of whole cells or organisms.
With the help of AI, the scientists then experimented with billions of body shapes so that the xenobots could more efficiently reproduce. They found that the 'parent' xenobot is C-shaped, it can find tiny stem cells in a petri dish. They then collect hundreds of cells into their mouth, and within a few days, the bundle of cells will become the new xenobot.
Xenobots are very early technology right now. It looked like a 1940s computer and didn't have any real-world applications yet.
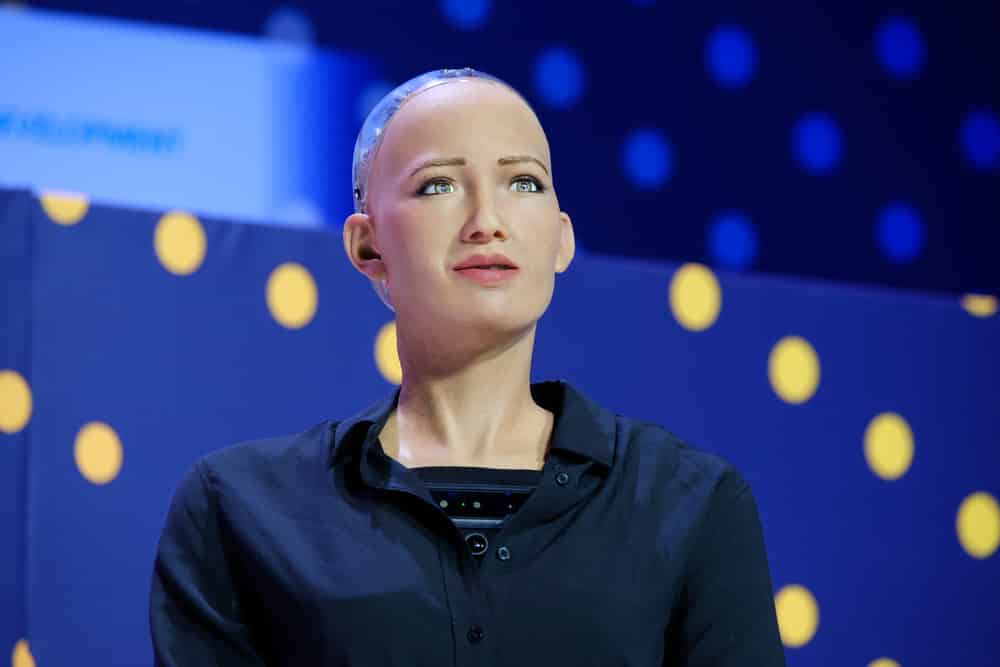
In fact, AI technology can have incalculable consequences for humanity, with the risk of replacing humans in the future. Before that, in 2017, the story of Sophia (operated by an AI system) became the first robot to be granted legal citizenship (even more rights than women in this country). stir up public opinion. The humanoid robot Sophia, who is a Saudi citizen, has made some controversial statements, but most recently, a statement from Robot Sophia left the world speechless : I want to have it. a robot child and start a family.
In a conversation with David Hanson, the creator of this robot, said that Sophia will destroy humans. Of course, that has caused anxiety, because since the early days of robots and AI technology, people have feared that they will rebel against humanity.
The robot is also controversially appearing as a lecturer on science and technology topics, appearing alongside celebrities in video conferences, TV shows and universities. study around the world. In early 2021, Hanson Robotics announced that it would start producing hundreds of robots using AI technology like Sophia.
- Discovering many cosmic mysteries, people yearn to find new worlds
- American 3D robot design know how to transform and jump high
- Robot revolution in the field of medicine
- Successfully built a 'live' robot from an African frog cell
- This is the robot used to destroy the killer of 5 American police last week
- Russia introduces the new generation humanoid robot SAR - 401
- Great robot war will happen in 2016
- Japan has successfully built a robot that can sweat to cool off
- Inventing tissue-like materials living with 3D printers
- The first robot with citizenship that once said 'destroy humanity' is about to have more 'em'
- Fire fighters in the world
- Termites do not necessarily have to reproduce sexually
 The world's first sexless AI voice
The world's first sexless AI voice This cool t-shirt will make you invisible to AI
This cool t-shirt will make you invisible to AI AI can predict personality only through selfie photos
AI can predict personality only through selfie photos The world-famous chess player lost to Golaxy before, artificial intelligence 'made in China'
The world-famous chess player lost to Golaxy before, artificial intelligence 'made in China' Good news: New cancer drug discovered that causes cancer cells to 'starve'
Good news: New cancer drug discovered that causes cancer cells to 'starve'  Why do we get older when cells are always replicating?
Why do we get older when cells are always replicating?  Shocking Research: Human Memory Doesn't Exist Only in the Brain
Shocking Research: Human Memory Doesn't Exist Only in the Brain  Reasons for easy weight gain: Obesity has 'memory' and retains mechanisms in cells
Reasons for easy weight gain: Obesity has 'memory' and retains mechanisms in cells  What happens to cancer cells after they die?
What happens to cancer cells after they die?  New Breakthrough: 'Hack' Tumors, Turn Cancer Cells Into Pills
New Breakthrough: 'Hack' Tumors, Turn Cancer Cells Into Pills 