Find out where to store fear memories in the brain
Millions of adults are suffering from anxiety disorders, including persistent worries that affect their daily lives. Scientists have now identified the area of the brain that controls fear , bringing hope to the birth of an effective treatment for these disorders.
US researchers have discovered a "circuit" that controls fearful behaviors and memories in the mouse brain, revealing how how anxiety disorders can develop. It is a group of nerve cells that form paraventricular nuclei of the thalamus , particularly sensitive to stress, which acts as a sensor for both physical and psychological stress.
The team conducted experiments to see if the PVT region affected the recognition and memory of fear in mice. They discovered that the PVT region was especially activated when the animals experimented with fear or recalled scary memories.
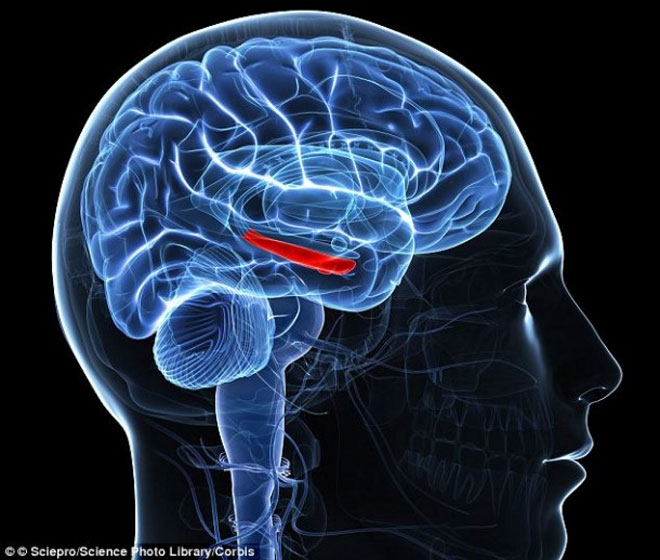
Cells in the PVT region extend into the amygdala of the brain (the area marked in red), which has a key influence on recognizing and remembering the fear of the subject.(Photo: Corbis)
According to experts, nerve cells from the PVT region extend into the central amygdala of the brain. Breaking this connection will significantly reduce fear awareness.
The team believes that, because the connection between the PVT region and the central amygdala region is a key component of recognizing fear, we can use it to attack the disorder. concerned.
Based on the above findings, the scientists looked at data on patients with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) to identify chemical substances that can link PVT and the amygdala region. center. They focused on a molecule called BNDF , which is involved in anxiety disorders and plays an important role in activating the production of new neurons as well as new connections between this cell.
Previous studies have shown that patients with anxiety disorders have mutations in BDNF, referring to this molecule that may affect recognition and memory of fear. Through mouse experiments, US experts confirmed, the existence of BDNF in the central amygdala activated the nerve cells of the brain region, causing the mice to "be brave", reacting fearfully. It also leads to the formation of long-term fearsome memories.
In a separate study, New York University psychologists found that the bright yellow curcumin compound in turmeric helps prevent the storage of new fear memories in the brain as well as eliminating signs. Scary memories are available. Experts hope, this discovery will lead to the creation of a new treatment for people with mental disorders.
- Find a way to help your brain overcome fear in your sleep
- Science gives way to new
- The new direction helps people to erase painful memories
- Will the brain be blown up when information is overloaded?
- Medical breakthrough: The pill forgets the past grief
- Find out how to permanently delete memories from your ex
- Identify areas of the brain that store social memories
- Discover how the brain creates memories
- The scent makes people recall memories
- Find new ways to erase painful memories
- Move all memories from one person's brain to another
- 8 bizarre fears of humans
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking