Harvard University developed a mobile vaccine without cold storage
Instead of cold storage of expensive, complex and demanding vaccines, people now only preserve raw materials that directly produce drugs or vaccines, and then when they need to be used are simply given Inlet water is already injected to patients. Called the "mobile molecular biology production technique " , the aforementioned drug preparation and storage technique was developed by researchers at Harvard University, promising to help deliver drugs to Outlying areas, for poorer regions, a simple and safer way.
Harvard's set of vaccine or portable drug products consists of two main components: a box containing chemical ingredients to synthesize the final product and another box containing "DNA instructions" for the task know which compounds to use to create the desired drug. When mixing these two ingredients together and adding water, people already have the medicine to be ready for injection. The team said that all types of drugs can be produced in this way, including vaccines for flu, flu, and vaccines against outbreaks and antibiotic peptides for treating the stain. open wound, .
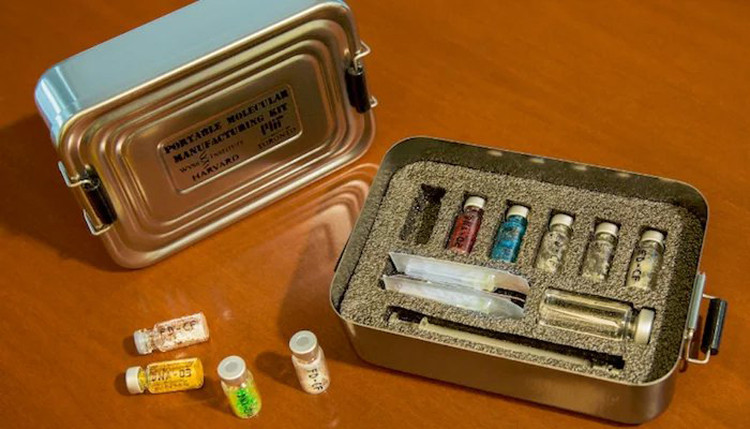
Set of vaccine preparation or topical products of Harvard University.
In the study, the team tried to use the above method to prepare a diphtheria vaccine. Although this is a fairly basic vaccine, imagine that in remote areas, without a medical center, without cooling facilities or even without power, it turns out that each dose of vaccine extremely worthwhile. Often such drugs need to be kept cold throughout the supply chain to ensure effectiveness. However, this time, the method of preserving materials and preparations when reusing can solve the problem.
Researcher Keith Pardee at the University of Toronto, also a member of the research team, said: "This approach can be applied without requiring too much training, contributing to the support of doctors. in remote areas or places without electricity ". It was previously known that the group has also developed a mobile cell synthesis system and, as a result, extremely stable systems, which can survive for at least a year at room temperature, are very cheap to produce. export.
Statistics from the World Health Organization WHO said that more than half of the world's people live in rural areas and on the other hand, more than 20 million babies are not vaccinated in the last year. measles. Therefore, this study, if completed and licensed, could be useful for many remote areas, poor or developing countries. At the same time, it can also be equipped for astronauts on space or even those on Mars to settle in the future.
- Harvard's HIV vaccine was initially successful on humans
- The first vaccine will soon be developed by AI in the world
- There will soon be a new vaccine against TB
- The first vapor film in the world
- Seagate launches wireless hard drive
- Vaccine for the rescue of tens of millions of people out of poverty
- Inventing a 10-year battery does not require charging
- Japan has developed a vaccine to prevent stroke
- Successfully modulated vaccine against dysentery
- Harvard University creates bacteria capable of absorbing CO2 and producing energy
- Develop methods to store blood and urine without chilling
- 9X invented a refrigerator that can save 1.5 million people every year
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking Hologram doctor - new solution for remote medical care
Hologram doctor - new solution for remote medical care  The snow melts, the Alps are strongly 'greening'
The snow melts, the Alps are strongly 'greening'  Scientists predict when a global catastrophe will happen
Scientists predict when a global catastrophe will happen  Most important marine areas are not preserved
Most important marine areas are not preserved  The paradox: Rural people are more obese than urban people
The paradox: Rural people are more obese than urban people  The scene is like an apocalypse in America when millions of bugs invade the city!
The scene is like an apocalypse in America when millions of bugs invade the city! 