People start going straight sooner than we think
Scientists have discovered the fossil skeleton of A.Afarensis of the Southern gibbon genus dating back 3.6 million years ago. The results of this study show that ancestors of humans began to walk straight ahead much earlier than we thought.

The first bone of the Kadanuumuu was discovered in 2005 in Afar, Ethiopia.Photos: scientificblogging.com
Scientists have named fossil skeletons that still hold about 40% of the completed excavations in Ethiopia's Afar Kadanuumuu (In the Afar language, the Kadanuumuu means "Big character"). Scientists think that the evolutionary history of humanity will have to be rewritten by the appearance of this "big character".
The Kadanuumuu is not the fossil skeleton of the only A.Afarensis found. Also in Ethiopia, in 1974, a fossil skeleton of this species was found in millions of years, dating back to 3.2 million years. That is the fossilized skeleton called 'Lucy', however, according to scientists, the date of the Kadanuumuu is earlier than "Lucy" for 400,000 years.
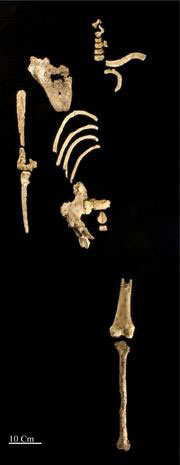
The "big character" Kadanuumuu began going straight 3.6 million years ago.Photo: Nature.com.
Yohannes Haile-Selassie, an ancient anthropologist at Cleveland Museum of Natural History, who heads the research program, said the skeleton of the Kadanuumuu still retains leg bones, ribs and pelvis. Compared to the ancient African gibbons, the Kadanuumuu is more modern. This shows that, at that time, human ancestors began to go straight. Although the skull has not been discovered yet, the skeleton is able to store parts that were not found during the excavation of the 'Lucy' skeleton."The important thing is that the skeleton is intact with the ribs and shoulder blades ," said Carol Ward of the University of Missouri, Columbia state .
In 2005, Alemayehu Asfaw, a member of Haile-Selassie's research team, discovered a piece of the arm bone of the Kadanuumuu. For the next four years, scientists unearthed the shoulder blades, ribs, collarbone and neck bones of the Kadanuumuu.
This is the first time that these bone parts have been discovered on the same individual fossil of southern ape species. In addition, the researchers found pelvic, arm and thigh bones.
Haile-Selassie said, the height of the Kadanuumuu is about 1.5-1.7m, higher than 'Lucy' about 30%. The shoulder blades of the Kadanuumuu are very similar to the shoulder blades of chimpanzees or humans but unlike the shoulder blades of chimpanzees. In addition, the second rib curvature of the Kadanuumuu is quite similar to that of modern humans but is also different from chimpanzees.
Haile-Selassie thinks that this study shows, 'Lucy' and maybe her 'ancestor', Kadanuumuu "stuff" almost went straight like a modern person. So in the evolution of mankind, the time when people start going straight may be much earlier than previous conclusions.
- Curved legs turn into straight legs: It turns out people have suffered this much
- The reason people go straight: It's too hot!
- Find the longest sea in a straight line
- Firecrackers use straight anti-current engines
- Will world oil output reach its peak next year?
- Straight line is not the fastest way?
- Device to diagnose stroke in 10 minutes
- People who sleep less easily die early
- 'Super drag Vector' cut super straight paper
- Is straight or curly hair the easiest to tangle?
- Crustaceans start eating synthetic resin
- Why does the plane never fly in a straight line?
 Discovered an ancient centipede fossil 99 million years old
Discovered an ancient centipede fossil 99 million years old Discovered bat-like dinosaurs in China
Discovered bat-like dinosaurs in China Discovered a 200-year-old bronze cannon of the coast
Discovered a 200-year-old bronze cannon of the coast Discover 305 million-year-old spider fossils
Discover 305 million-year-old spider fossils