Present the world's first artificial antibody
American chemists have released the world's first artificial antibodies, able to adhere to disease-causing cells and help direct the body's immune system to cope with them.
The artificial antibodies of the Yale University team (USA) have simulated natural antibody activity, which binds diseased cells and bacteria into the blood, and encourages white blood cells. destroy them.
The patent team claims that artificial antibodies that can be stored at normal temperatures can provide new and convenient treatments for countless diseases, including infections, cancer and HIV. .
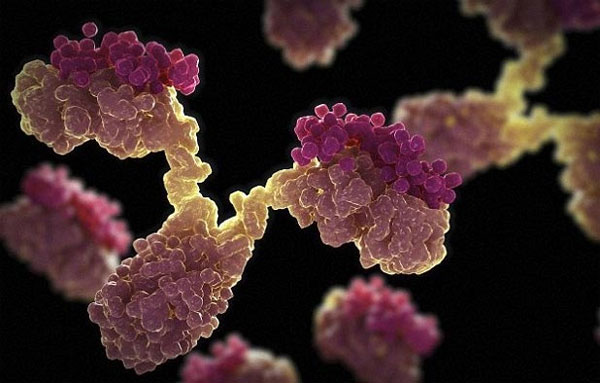
Natural antibodies are Y-shaped proteins (as illustrated) that are patrolling in the body to detect disease.(Photo: Daily Mail)
Dr David Spiegel, a chemist involved in the development of artificial antibodies, adds that these molecules can be used in tablet form as pain relievers or antibiotics. He and his colleagues used them to make an artificial molecule that attacks prostate cancer.
Dr. Spiegel explains: "Unlike natural antibodies, our molecules are synthetic organic compounds that are approximately one-twentieth the size of natural antibodies. They are rare. "The ability to cause undesirable immune reactions by structure. They are also thermally stable and have the potential to be taken orally, like traditional small molecule drugs."
Doctors have used antibodies to treat human diseases - monoclonal antibody therapy. This is essentially a form of immunotherapy, using natural antibodies that come from laboratory nourishing cells. However, these antibodies tend to be large-sized molecules, sensitive to temperature changes and need to be stored carefully.
Due to their large size, the antibodies also need to be used by injection. They work by marking diseased cells and forcing the immune system to destroy these cells.
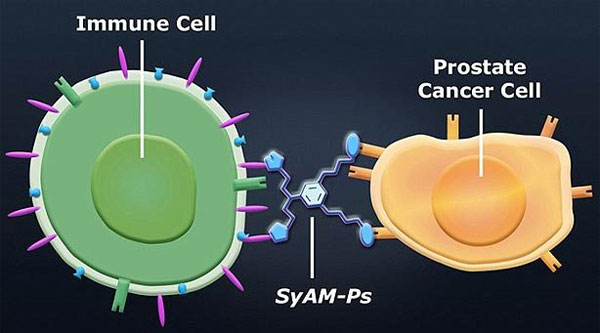
The team used artificial antibodies SyAM-Ps adheres to antigens on the surface of prostate cancer cells, before connecting with immune system white blood cells to kill infected cells.(Photo: Daily Mail)
In the human body, natural antibodies are Y-shaped proteins, produced by blood cells in the blood, in billions. Each such molecule contains adhesion structures on unique molecules called antigens on the surface of foreign invasive cells , helping them to identify non-body cells.
By forming blocks around invasive cells, antibodies can neutralize them, and lead to white blood cells from the immune system that will destroy the latter.
The antibodies that make SyAM-Ps invented by Dr. Spiegel's team do the same thing. However, the size is only 1/20 the natural antibody means that they can pass through the intestinal wall. Therefore, they can be used as oral tablets, instead of injections.
Currently SyAM-Ps has only been used to deal with cancer tissues in the laboratory, but researchers hope to soon test them on animals. If successful, it could lead to human clinical trials a few years later.
- Breakthrough: Detecting antibodies can kill 99% of the HIV virus strain
- America: Detecting new antibodies that treat 7 types of cancer
- This AI system will create images from the input text
- Effectively testing the vaccine for Zika virus in monkeys
- Artificial intelligence
- The truths always amaze you about the biological world
- France blocks 'gate connecting the worlds'
- Semi-artificial microorganisms - New breakthrough in molecular biology
- Successful development of antibodies that treat Ebola
- Successfully developed an artificial arm that can feel real
- Detects antibodies that neutralize HIV virus
- Find new antibodies, disable 98% of the HIV / AIDS gene sequence
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking