The feminine syndrome has testicles
This syndrome is a female form but the female genotype is actually a male genotype . Patients have external mammary and genital glands like those of women, but they are amenorrhea when they reach puberty. People with this syndrome are usually found only when there are problems with infertility or accidental visits to other patients.
Causes of female testis
Androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS: androgen insensitivity syndrome) is also known as androgen resistance syndrome , a collection of disorders related to gender differentiation. AIS occurs due to the mutation of the AR gene. This gene regulates the sensitivity or reception of androgen receptors. Without the effects of androgen, the body will develop towards women under the action of estrogen. The result is that while the testicles still develop normally and produce normal androgen, the patient's external appearance is still developing in a female direction. Therefore, this disease was formerly known as femaleized disease with testicles.
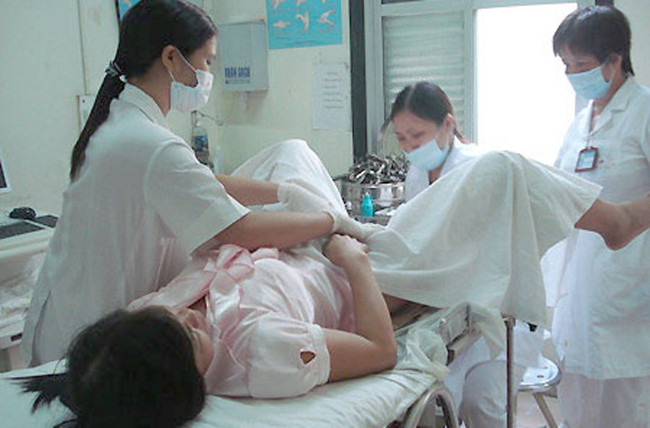
Clinical examination revealed that AIS patients had no uterus and ovaries.
Disease manifestations are easily overlooked
At birth, a baby with AIS is like a normal girl, with no hint of suspicion of suspicious chromosomes (NST) or abnormal testosterone levels. Puberty tends to start softer than other girls. Breast development, pelvic structure and body fat distribution occur like other girls.
However, the patient has little or no pubic hair, or male hair distribution. The facial skin of the patient is usually more beautiful than his peers, without acne because the sebaceous glands do not respond to the stimulation of androgen. In general, puberty is not much different from other girls, except that the patient will not have periods. Because menstruation usually occurs about 2 years after breast development, people often don't worry about girls having no periods until they are 14 or 15 years old.
Clinical examination revealed that the patient had sparse pubic hair or had absolutely no pubic hair, the external genitalia was a female with a short vagina, no cervix. Because the patient does not have a uterus, the vagina usually ends up being a sac, with absolutely no sympathy for the inside. Ultrasound did not see the uterus and 2 ovaries. The patient has absolutely no fertility. It is possible to feel a bulge in the inguinal area raised by the testicles. Most are not palpable because the testicles usually remain in the abdomen.
When suspecting patients with this syndrome, just performing the chromosome will help us confirm the diagnosis.
Is treatment difficult?
The most difficult step in treatment is how to diagnose a diagnosis for patients and families . Because this condition is accompanied by complications that a permanent patient cannot have children and gender inconsistency makes a patient's partner feel anxious, the psychology of people with the disease is very vulnerability. Therefore, deciding how to notify the diagnosis to patients should put the patient's benefits first.
Most patients will feel confused and suffering, dissatisfied. Therefore, the strategy of counseling and mental support for patients immediately after that with the system approach should be carefully prepared in advance. Many women with AIS feel much better when they are helped to contact people with the same disease.
Other treatment problems
- Vaginal enlargement: For women who have difficulty with vaginal sex, the vagina can expand itself gradually because it is able to relax after a long period of spousal activity . Surgical vaginal reconstruction can be done for adults but can also cause some complications.
- Testicular removal: This is a controversial issue. The benefit of testis until after puberty is that no exogenous endocrine use is required. This happens because testosterone produced by the testicles will turn into estrogen. The main argument about removing the testicle is that the testicle in the abdomen may develop into a benign or malignant tumor.
In addition to this, many patients say that after the testicles are removed, they do not feel as normal as before, such as a physiological reduction.
- Estrogen replacement: If the testicle is removed, estrogen should be used to support puberty, bone growth and complete maturation. Because the patient has no uterus, no progesterone is needed.
- Anti-androgen syndrome is a rare and family-like syndrome. The diagnosis of this syndrome is not difficult. However, in terms of treatment, until now, medicine is still helpless before pathologies related to genetic abnormalities in general and this syndrome in particular. Hopefully in the future, AIS will be studied more and we will find the best new treatments for patients.
- Plastic makes men more feminine
- Men with large testicles are more likely to develop cardiovascular disease
- What to know about 'feminine hygiene solutions'
- Cure infertility with artificial testicles
- Absolute feminine animals in nature
- The disease syndrome makes people special
- Strange fear syndrome that you may be suffering from but don't know how to call
- Men are 'feminine' easy to achieve at work
- Decode the 10 most macabre mental diseases that people have
- Detection of Down syndrome when the fetus is only 11 to nearly 14 weeks old
- The truth about human 'unusual' eating syndrome
- What is IBS syndrome?
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking How to deal with dangerous cardiovascular situations?
How to deal with dangerous cardiovascular situations?  Japan confirms the first case of thrombocytopenic fever transmitted from person to person
Japan confirms the first case of thrombocytopenic fever transmitted from person to person  Top 5 medical therapies are gradually coming out of fiction movies
Top 5 medical therapies are gradually coming out of fiction movies  The 32nd person in Vietnam infected with corona virus
The 32nd person in Vietnam infected with corona virus  For the first time in the world, Vietnamese doctors transplant the hands of living people to patients
For the first time in the world, Vietnamese doctors transplant the hands of living people to patients  Virus Corona: How does Covid-19 change over the day?
Virus Corona: How does Covid-19 change over the day? 