What is the Tor browser and how does it protect your privacy?
If you're new to internet privacy and security, you've probably heard of something called Tor - an internet connection software that comes with its own browser that's now quite widely used.
Tor is very popular among privacy-minded tech connoisseurs for its reliable encryption capabilities, while helping users conceal their movements on the internet.
At first glance, the concepts surrounding Tor can be quite vague and confusing. But don't worry, things are much simpler than you think.

Tor is a type of network that connects to the internet with its own internet browser.
What is Tor?
In the mid-1990s, as the US Navy was looking for secure ways to transmit sensitive intelligence, a mathematician and two computer scientists at the Naval Laboratory (NRL) something called is "onion routing ". It's a new kind of technology that protects your internet traffic with multiple layers of privacy. By 2003, The Onion Routing project, Tor for short, was widely available to the public, and its huge network of users - the "engine" that ensured the Tor's existence - just keeps growing.
Today, thousands of volunteers around the world keep their computers connected to the internet to form the Tor network by becoming "nodes" or "relays" for your internet traffic.
At its most basic level, Tor is a type of network that connects to the internet with its own internet browser. Once you connect to the internet using the Tor browser, your internet traffic will be stripped of the first layer of identifiers that enter the Tor network, and will then be routed back and forth between the aforementioned relay nodes. , which encrypts and privates your data layer by layer - like an onion. Finally, your internet traffic will go to the end node (exit node) and leave the Tor network to go to the open web.
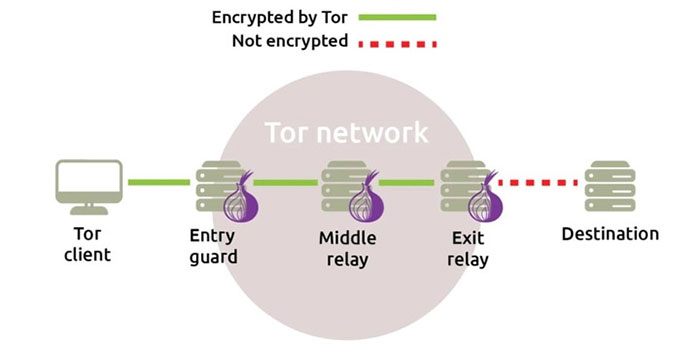
Once you're in the Tor network, tracking your traffic is nearly impossible.
Once you're in the Tor network, tracking your traffic is nearly impossible. And once you leave the Tor network via an exit node, the website you view (assuming it has HTTPS in front of the address) won't know where in the world you're visiting from, making your browsing a breeze. more private and better protected.
How to use Tor
Browsing the web with Tor is pretty easy . Just go to the official website and download the Tor browser. Follow the installation instructions just like you would with any other program. When you open Tor for the first time, the program will ask you to configure the connection (if you are in a country where Tor is banned, like China or Saudi Arabia), or work immediately. Once you press the connect button, Tor will spend a few minutes looking for a series of relays to connect you to.
But once you're on the Tor network, you can use it as you would any other browser. You will also be prompted to review your Tor browser's security settings. If you want to maximize privacy, it's best to leave the default settings as they are.
If you're experiencing slower-than-normal connection speeds, you can ask Tor to check if there's a faster route to the website you want to see. In the upper right corner of the Tor browser, click the 3-dotted menu icon and select New Tor Circuit for this Site.
The privacy-focused browser Brave also has an option that allows you to direct traffic through Tor when you open an incognito window.
Disadvantages of using Tor
Since Tor is a network maintained by volunteers, speed is often the most common issue . For example, in the process of your internet traffic going from one node to another, you will most likely notice a loss in speed compared to using most virtual private network (VPN) services. charges. This is most noticeable if you're trying to watch Netflix over Tor or make VoIP calls, or make video calls through an app like Zoom. Tor technology wasn't actually developed to deliver the smooth video and audio experiences you'd expect.
Speaking of videos, there are some limits to how much privacy Tor can guarantee you if you activate certain multimedia plugins, like Flash . Similarly, a browser's JavaScript plugin - which allows you to view multimedia content embedded in many websites - can still leak your IP address information. The file Torrent downloading via Tor will also put you ahead of the privacy risks. Because of these risks, Tor's default privacy settings disable these types of plugins.
If you just want to surf the internet normally with a browser that hides your traffic from owls, Tor is probably not the best choice because of its slow speeds and poor compatibility with owls. most embedded multimedia content. But if you care about privacy when searching for a particular topic on the internet (and you don't have a VPN), Tor is probably the best choice.

Ideally, you should be familiar with both types of software before combining them.
Does Tor work with VPNs?
In some cases yes. Most of the time, though, you'll have to know how to configure your VPN connection to work in harmony with Tor. If not set up correctly, you can make both Tor and VPN less effective at protecting your privacy. Ideally, you should be familiar with both types of software before combining them.
The upside is that if you successfully combine Tor and VPN, you will have an extremely useful shield. While Tor protects your internet traffic, a VPN can take care of encrypting the internet traffic of any other apps running on your device.
- Google calls for a law to protect global privacy
- Acoo browser: mesmerizing web browser
- Why is the browser running slow and how to fix it?
- Google's worst privacy policy in the world
- How to change the default browser on Windows 10
- Create your own browser
- Austrian robots protect the wearer
- Top most downloaded browsers for Android
- Hide Window Plus - Add a tool to protect your privacy
- Better browsing with Avant Browser
- Browzar: Browser with
- The IE browser was officially replaced by Spartan
 What is the Snapdragon SiP chip?
What is the Snapdragon SiP chip? How to create a yellow circle around the mouse cursor on Windows
How to create a yellow circle around the mouse cursor on Windows Edit the Boot.ini file in Windows XP
Edit the Boot.ini file in Windows XP 3 ways to restart the remote computer via the Internet
3 ways to restart the remote computer via the Internet