Why are raindrops different sizes?
By filming a falling raindrop, scientists in France have explained why raindrops have so many different sizes. Writing in the journal Nature Physics , the group of scientists described how the raindrops were deformed and broken during falling.
Its fragments fit into the size and distribution of raindrops in natural showers. Scientists previously thought that raindrops collided when falling, and these interactions created the size of raindrops. But the head of the study, Dr. Emmanuel Villermaux of the University of Aix-Marseille, explained that there is ' deficiency ' in this idea. ' Rain drops don't seem to touch each other often. They are very far apart, seem to fall alone and do not "see" the neighboring droplets, " he said.
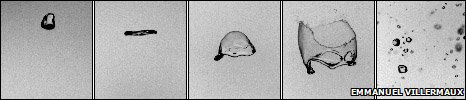
A raindrop deforms when falling in the air and eventually blooms and explodes (Photo: Aix-Marseille University)
With a high-speed camera, Villermaux and his colleagues only filmed a single rain drop - diameter of 6mm. They recorded the air resistance that distorted it and eventually broke out. The raindrops are large, round, gradually flatten and when they get bigger they ' catch ' the air in front to form a bag upside down. Eventually this bag expands and explodes into smaller particles. This happens because too large and heavy particles cannot be preserved. Each particle is large, heavy accelerates when dropped and ' must shift air molecules ' on its way, Villermaux explains.
' When ruptured, raindrop fragments are the same size as the raindrops we see in the rain, ' Villermaux concluded.

(Photo: Guim.co.uk)
- Why are Asians often smaller than Europeans?
- Power generation by rain
- The magical beauty of the rainbow
- Compare the size of the largest prehistoric animals
- Convert image sizes and formats with EvJO Photo-Image Resizer
- Mysterious blood rain phenomenon in India
- Animal weight today compared to ancient relatives
- 'Spray' condoms meet all sizes
- 'Blood rain' in India - evidence of aliens visiting Earth?
- How to choose a large computer screen
- How many meteors fell on Western Canada?
- The snake is as long as a bus
 Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity?
Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity? Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer
Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer Lightning stone - the mysterious guest
Lightning stone - the mysterious guest Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance
Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance