9 frequently asked questions about peptic ulcer disease
Gastric ulcer is considered a disease of civilized life. The more people go around racing with time and work, the more disease will develop. There are 1 out of 10 people suffering from stomach pain.
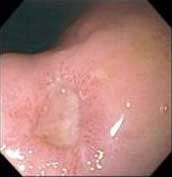
Stomach ulcer (Photo: bvdaihoc)
Most cases of gastric ulcers are caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (HP). This bacterium is present in 90% of patients with duodenal ulcers and in 70% of gastric ulcers. This discovery brought the Nobel Prize to Australian scientists Marshall and Warren.
What is gastric ulcer?
The stomach uses gastric juice to fragment food. To protect the stomach wall from the attack of hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice, a thick mucous membrane covers the inside of the stomach. But when the regeneration of mucous cells is disordered and stimulated by the gastric juice, it creates ulcers a few millimeters in diameter. Duodenal ulcer occurs in the colon, the connection point between the stomach and small intestine, accounting for 90%. Ulcers located in the stomach can lead to serious complications.
What causes ulcers?
For a long time, it was thought that the origin of gastric ulcer was the mental factor. But today, it is known that 99% is caused by HP bacteria. This discovery has revolutionized the treatment of gastro-duodenal ulcers by destroying this bacterium.
However, ulcers are also possible due to the effects of frequent aspirine use or other non-streoid analgesics. This group of drugs is toxic to the stomach and reduces the natural defense mechanism of mucous membranes. The use of these group drugs to treat pain will contribute to increased ulcer status.
What are the symptoms of ulcer manifestations?
Ulcers are accompanied by pain such as cramps, heat, constriction in the stomach. The pain appears about 4 hours after a meal and can last up to the next meal. Besides, there may be combined symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, digestive disorders. Supplying food to the stomach often helps relieve pain. Symptoms last a few days and then become painful periodically.
When to go to the doctor?
If the pain cannot be relieved when using over-the-counter stomach pain relievers, if it reappears many times during the day and night, it is advisable to seek medical care for early and effective treatment.
What are the factors that aggravate stomach ulcers?
There are many factors that increase the severity of the ulcer, although not the cause of the ulcer: tobacco addiction, alcoholism, heavy use of coffee, frequent stress, non-steroidal analgesics and corticosteroids.
The above factors need to be removed once ulcers are diagnosed. Follow a balanced diet, use plenty of vegetables to provide fiber (fiber), avoid too much fried or spicy fried foods. Need time to eat; Hurried meals will make the gastric juice produce much more painful sores.
How to diagnose stomach ulcers?
The diagnosis requires a fibroscopie scan to see the ulcer and get a biopsy of the mucous membranes. The patient is not very comfortable with this method, so it can be tested indirectly by inhalation test.
How to treat?
The most basic is to use the drug at the same time to reduce the secretion of gastric juice and antibiotics to destroy HP. Two commonly used pharmaceutical groups:
- Anti-secretion to prevent the production of hydrochloric acid and instantiate mucous lesions: it is a proton pompe blocker that is usually used for 4-6 weeks.
- HP antibiotics are usually amoxicillin and clarithromycin for at least a week. For several days, symptoms disappeared but treatment should not be discontinued because the disease is easily recurrent with the HP strain resistant to the therapeutic dose and the old antibiotic.
When do you need surgery?
With the progress in therapeutic therapy, only fewer and fewer surgeries are needed. However, in the case of gastric hemorrhage, the surgeon will have to sew blood vessels or sew the ulcer.
In stomach ulcers, it is worrisome to develop into cancer. After repeated re-treatment without proper treatment or in case of suspicion of ulceration, the surgeon may remove part of the stomach where the ulcer is then depending on the situation, possibly simultaneously cut vagus nerve to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid
What do complications include?
If left untreated, ulcers can develop complications such as stomach bleeding or gastric perforation. Hemorrhage can be identified in blood vomit (red or black) or black blood in the stool. Hemorrhage indicates severe damage to blood vessels.
Perforation of the stomach is often accompanied by severe abdominal pain, requiring urgent examination. They often carry peritonitis. Patients should be hospitalized and surgically intervened. There are patients without severe pain but still bleeding.
- O-type people are most likely to develop stomach ulcers
- Implementing this diet, stomach ulcers will no longer be afraid of the disease
- Frequently asked questions about defecation habits that you are not sure yet
- 9 common questions in children and how to answer scientifically and reasonably
- 6 important things about stomach ulcers everyone needs to know
- Asteroids hit Earth: Don't be too afraid ...
- Create the stomach in the world's first laboratory
- New pathogen from peptic ulcer disease
- Why have nausea when brushing your teeth?
- The naive questions that people search on Google and the scientific answer
- Climate change threatens human life
- Going out several times a day, what is the cause?
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking