Research: Fasting 24 hours helps strengthen stem cell regeneration
For decades, many researchers have pursued an idea: Eating diets, reducing even calorie-fasting plans is the key to a healthy life and long life.
Now, they have found evidence for this effect. In a new study examining the effect of fasting in rats, scientists found a 24-hour fasting period that most likely turned on a switch to boost regeneration. Stem cells in the intestine.
These intestines are things that deteriorate when we get older and cannot reproduce effectively afterwards.
Worth mentioning is that bowel stem cells play a very important role in helping us maintain healthy tissue and fight disease. Therefore, if fasting for a day can reactivate the process of regenerating these stem cells, it will be a miraculous effect, well worth exploring.
The study was published in the journal Cell Stem Cell.
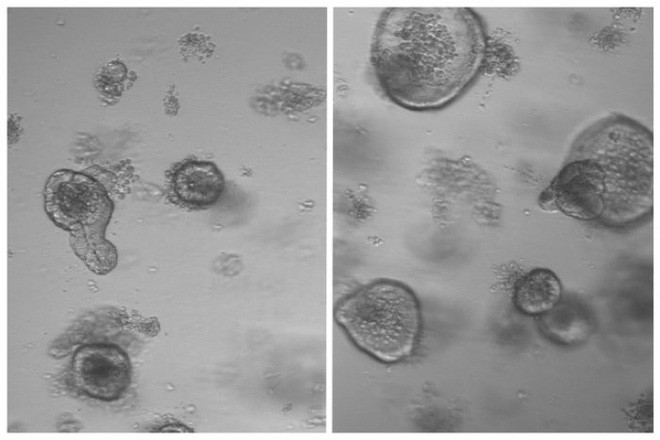
Fasting for 24 hours helps strengthen regeneration of stem cells in the intestine of mice.
'Fasting greatly affects the intestinal tract, including strengthening the regeneration process in this organ, as well as increasing the ability to resist any disease entering the intestine, such as infection or cancer. 'letter,' biologist Omer Yilmaz of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) said.
"This study provides evidence that fasting creates a metabolic metabolism in intestinal stem cells, from the use of carbohydrates to fat burning."
Accordingly, this change not only means that cells will use fat as a source of energy instead of carbohydrates, but it also enhances cell function.
Scientists call intestinal stem cells 'dragons', implying they have important functions and serve the intestinal and body functions for a long period of life.
Normally, these cells regenerate the intestinal mucosa every 5 days. But when fasting causes transitions, the regeneration process can happen faster.
In the lab, Yilmaz's team took intestinal stem cells from mice that had been fasting for 24 hours and fed them in the nutrient medium to form cells like small intestine cells called organoids.
In doing so, they found that the reproducibility of stem cells taken from mice that starved for 1 day was twice that of normal non-fasted mice.
According to medical researcher Maria Mihaylova, a member of the research team: 'It is clear that abstinence has a really big effect on the ability to form organoids from stem cells. This is something we have seen in both young and old mice, and we really want to understand the molecular mechanisms that promote this. "
To find out, Mihaylova's group decoded the messenger RNA of the stem cells from fasting mice, and found that 24-hour fasting triggered transcription factors called proliferator peroxisome activation receptors (PPAR). ) . This receptor activates genes involved in the metabolism of fatty acids.
In this case, the activation causes cells to break down fatty acids instead of glucose, and promote cell regeneration. When they blocked PPAR activation, enhanced regeneration finally ended.
But that contains everything that the research team finds out. By injecting a molecule called GW501516 into mice to activate the effect of PPAR, this dose of stimulation was able to simulate some of the beneficial effects of fasting in mice.
"It is also very surprising," said Chia-Wei Cheng, one of the researchers. "Just activating a single metabolic pathway is enough to reverse certain aging patterns."
If there is a simulated dose of fasting, it can help people, often patients, not be able to do this. For example, older people, cancer patients who have a debilitating body are those who cannot fasten to activate health effects, while they need them very much.

There have been many studies showing the health benefits of fasting.
Of course, these are just initial results. There will still be many things waiting for researchers to explore, before we understand the extent of this switch and its function - Whether this effect can be easily activated in humans like in mouse or not? Do you only need 24 hours of fasting to regenerate your intestines?
Questions have no answers. However, when the problem is clarified, we will face an opportunity to develop drugs that promote intestinal function and overall health, increasing life expectancy.
"This work is consistent with a rapidly growing field, demonstrating that nutrition and metabolism have a profound effect on cell behavior and this may be related to human illness. " , Jared Rutter, a biochemist at the University of Utah, who was not involved in the study.
- The new invention turns fat into bone
- How to treat nerve damage with stem cells
- Stem cell therapy will help restore lung tissue
- Vietnam isolated bone marrow stem cells
- Turn fat into bone
- The US dropped the ban on funding for stem cell research
- Mexico focuses on promoting the creation of stem cell banks
- Regenerating gums with stem cell technology
- America successfully recreates bones from stem cells
- Be careful about stem cell therapy
- LEARN ABOUT ORIGINAL CELL (Last part)
- It was possible to transplant stem cells from one person to another
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking