Russia discovered where the
Astronomers in Russia have just discovered that the "rest" of an object is said to be the Soviet probe Mars 3 that landed on the surface of Mars in 1971. With images sent from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) satellite, a research team found at least four components of the vessel, including speed reducers and landing modules.
Mission to explore the former Soviet planet Mars 2 and Mars 3 using two identical ships, each equipped with a low-altitude trajectory transport / approach module /landing. Mars 3 was launched on May 28, 1971 from Baikonur Cosmodrome - the world's first and largest spacecraft launch station and landed on Mars on December 2 of the same year. While the Mars 2 ship disappeared when it dropped in height due to a dust storm sweeping through the planet, Mars 3 survived and it named itself a record book when it became the first spacecraft to successfully land. Mars. Unfortunately, success only stopped on the landing side because the ship was broken two minutes later.
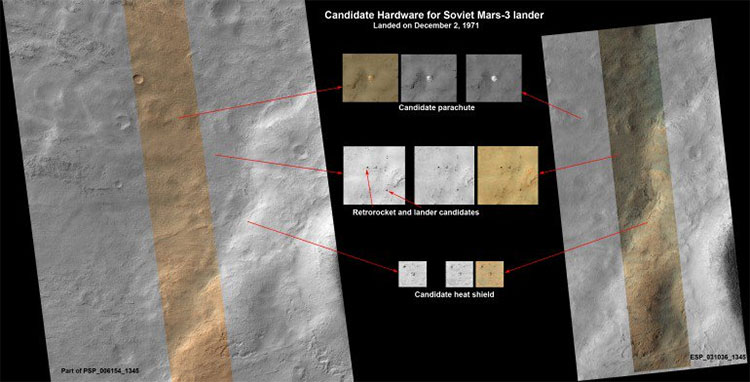
Images from the MRO show traces about Mars 3.
Vitali Egorov, the largest community leader (Vk.com) in Russia on the Curiosity mission, announced that Mars 3 may have been found by members of the site. This astronomical community soon searched for a 1.8 billion px resolution photo taken by HiRISE camera on MRO in November 2007 to an area where the Mars 3 ship landed. Based on the models reconstructed by Egorov about the hardware components of Mars 3, the possibility of 4 components is detected.
Egorov said: "I want to draw people's attention to the fact that today's mission to explore Mars is possible for anyone. At the same time, we were able to connect with the calendar. history of my country, an event that took place many years ago through photos from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter ".

Another image of Mars 3.
Alexander Basilevsky from the Vernadsky Institute of geochemistry and chemistry analysis, Moscow and the astronomer adviser contacted the MRO HiRISE system researcher - Alfred McEwen from Arizona University, Tucscon to suggest a The next image was taken on March 10, 2013. The new image of the object appears brighter - the possibility of better illumination thanks to the tilted surface of the object or the upper layer of dust that has been blown away to Reveal bright components, such as speed reducer.
The team found four components of the low / amphibious module, which included a 7.5 m / 11 m expansive parachute, an anti-heat pad, a module High altitude and the Mars 3 lander.

Sketch image of Mars 3.
"When combined, the composition of the components on the ground shows a surprising relevance to what we can predict when Mars 3 landed, but it doesn't exclude the Other solutions for these components The analysis of data and subsequent images to better understand the object's three-dimensional shape will clarify all questions, " McEwen said.
High-altitude / landing modules are connected to orbit during Mars 3's "drift" from Earth to Mars. The rest of the module will be in orbit to serve meteorological research and relay data from lander ships. As for the lander, it has a 1.2 m diameter sphere with four triangular landing legs that automatically open after landing to reveal two television cameras, a mass spectrometer and thermal sensors / wind. The ship also carried a pillar with a Soviet badge.

Prop-M self-propelled ship.
Another notable point in the history of the Mars 3 is that it is also equipped with the first self-propelled vehicle on Mars named Prop-M. This is a 4.5 kg robot that is tied to a lander with a 15 m communication cable. Prop-M is designed to be able to "walk" with two skis (pictured above) and it will move within the view of the TV cameras while performing the measurement with the dynamic meter and Integrated radiation density meter on board.
After a 3-minute drop in altitude on December 2, 1971, Mars 3 landed on a parachute and rocketed at the crater Ptolemaeus. 90 seconds after landing, the outer protective petal shell opens and the radio signal starts to transmit at 1:52:05 GMT but loses signal at 1:52:25 PM GMT. In this short time, Mars 3 tried to send a wide-angle image captured in low light and unknown details. The damage could be due to the giant dust storm sweeping across Mars that created a static charge and the phenomenon of photovoltaic discharge that destroyed electronic equipment inside the ship.
Documentary film about Mars 2 mission, Mars 3 Mars.
- Russia has just discovered a rare lichen
- Russia discovered the new island has never been known in the North Sea
- Discovering strange creatures in Russia
- 17 facts sounds like a joke about Russia
- Discovered a rare twelfth century mask in Russia
- Russia discovered a golden block of 2,400 years old
- Video: Meteorite plunges into eastern Russia and explodes
- Discover mysterious underground structures in Russia
- Discovered a tomb full of treasures in southern Russia
- Discovered albino porcupine in Russia
- Russia discovered a new Comet
- Russia discovered the apparatus dating back 400 million years
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people Revealing the first city on Mars, with enough space for more than 250,000 people to live
Revealing the first city on Mars, with enough space for more than 250,000 people to live  We could start building a colony on Mars with just 22 people!
We could start building a colony on Mars with just 22 people!  Amazing discovery of 4.5 billion year old alien ocean of life
Amazing discovery of 4.5 billion year old alien ocean of life  Mars' Surprising Effect on Earth's Oceans
Mars' Surprising Effect on Earth's Oceans  Was there nuclear war in ancient times?
Was there nuclear war in ancient times?  What happens to dead bodies on Mars?
What happens to dead bodies on Mars? 