The diphtheria and complications
Diphtheria is an acute infectious disease that occurs at any age and can lead to rapid death if not treated promptly.
Diphtheria causes major damage in the nasopharynx, throat, nose, larynx, skin and other mucous regions .
Diphtheria can be transmitted from infected people to others through inhalation (sneezing, coughing) and direct contact. The disease can cause nasal infection, throat death.
The good news is that thanks to the vaccine, the disease is less common or may be milder than before.
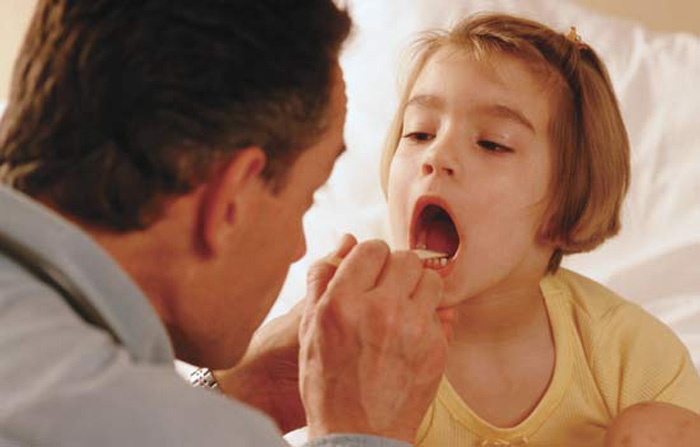

Children are subject to diphtheria
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms vary depending on the location, time and distribution of the toxin in the body and the immune status of the child. The incubation period is about 2-4 days, manifested by unpleasant symptoms such as headache, sore throat. Depending on the location of bacteria arising in the nose, throat or larynx, there are different clinical manifestations:
Diphtheria
It usually begins with a mild or bilateral runny nose, which lasts for several days, sometimes the nasal and bloody nose ulcers the lips and smells bad. Systemic symptoms may be mild but can still form a membrane on the nasal wall. Common disease in nursing babies.
Throat disease
Sudden child has a sore throat, headache and discomfort, and the pulse is too fast compared to a mild fever. A throat examination can easily see a false, gray-white false throat. If peeling this membrane will cause bleeding (which is a characteristic of diphtheria fake membrane).
Diphtheria
Usually, the diphtheria spreads down, the disease occurs in a nursing baby. Symptoms begin with a hoarse cough, then whistling, pulling the hollow of the breast, a frightened face. Signs of difficulty breathing are increasing, if not handled promptly can be dangerous to life.
In addition, diphtheria bacteria can cause eye, ear, vaginal and skin damage. Skin lesions are an important source of infection from one person to another.
 Diphtheria causes nose and throat infections that can lead to death
Diphtheria causes nose and throat infections that can lead to death
Complications of the disease
Complications of diphtheria: is an important cause of death in children.
Cardiovascular complications : It is toxic myocarditis usually occurs on Monday to Saturday. Expression: tachycardia, heart murmur, especially conduction disorders leading to cardiac arrest and death.
Neurological complications : Including partial paralysis of cranial nerves (No. 4, No. 10), which appear at the earliest on the 5th day, may include blurred vision, difficulty swallowing, nasal speech . Can be exported heart failure and vascular failure due to degeneration of vasomotor centers and arterial paralysis in the second or third week after illness.
Variation of peripheral neuritis : This is a late complication that occurs 12 weeks after local injury. Sometimes paralysis or simultaneous paralysis of diaphragmatic nerves, gastritis and hepatitis.
How to prevent disease
The best way to prevent diphtheria is to vaccinate your child according to the vaccination schedule . Children should be vaccinated 3 times at birth, each time separated by 1 month, then 1 year later repeated and after 5 years reminded again. However, vaccination is not always complete, but if it is given, the infection is milder and less complicated.
For people with diphtheria, need to isolate patients for at least 2 days after appropriate antibiotic treatment and wear masks when exposed. Also need to clean rooms, personal belongings, toys . with antiseptic solution.
In summary : Parents need to know how to detect early, when children get sick, they should bring their children to the hospital for treatment and treatment soon to avoid the unfortunate consequences of being late. This is a contagious disease that spreads quickly so when detected it should isolate children early.
- Sore throat: Very dangerous manifestations of diphtheria are outbreaks
- Find out the cause of the deadly
- How dangerous is diphtheria?
- Signs of identification and prevention of diphtheria
- 7 important vaccines minors should inject
- Stanford successfully developed AI that can predict drug-related complications
- Complications of bronchial asthma
- Dangerous complications of chickenpox that few people know
- Dangerous complications can occur when tonsils are removed
- The man lost both legs because of flu complications
- Eye complications due to the use of contact lenses
- Many adults have measles complications of encephalitis
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking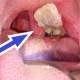 How to distinguish diphtheria and sore throat
How to distinguish diphtheria and sore throat  Signs of identification and prevention of diphtheria
Signs of identification and prevention of diphtheria  How dangerous is diphtheria?
How dangerous is diphtheria? 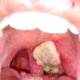 Sore throat: Very dangerous manifestations of diphtheria are outbreaks
Sore throat: Very dangerous manifestations of diphtheria are outbreaks 