The mirror was born about 600 BC. However, it was not until the nineteenth century that humanity could get mirrors like today .
8000 year history of mirrors
Mirror mirror image like?
When light hits the surface of an object and is reflected back into the eye, we can see it. In the picture below, the butterfly we see in the mirror is actually just a virtual image due to the eye being deceived.
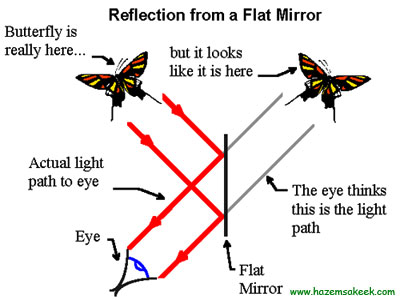
According to the laws of reflection, when a ray of light hits a flat surface, it is bounced off in a certain way, as if throwing a ball at a wall it will be reflected. The angle of incidence is also known as the angle of incidence. The intersection of the reflected rays from a point will form the image of that point.
The first mirror
The very primitive form of the mirror is probably the calm lake surface, the shiny stone face or the water in the containers. Interestingly, from about 722 BC onwards there appeared ancient Chinese characters that meant mirrors. It is jian or jing , meaning "a large tub full of water. " Since then, it has been shown that it was nature that gave people the first mirrors. This is also an important form that makes people have ideas based on and create mirrors later.
Some suggested that it was the Chinese who invented the mirror. However, according to some reliable evidence, the above judgment is not completely accurate.
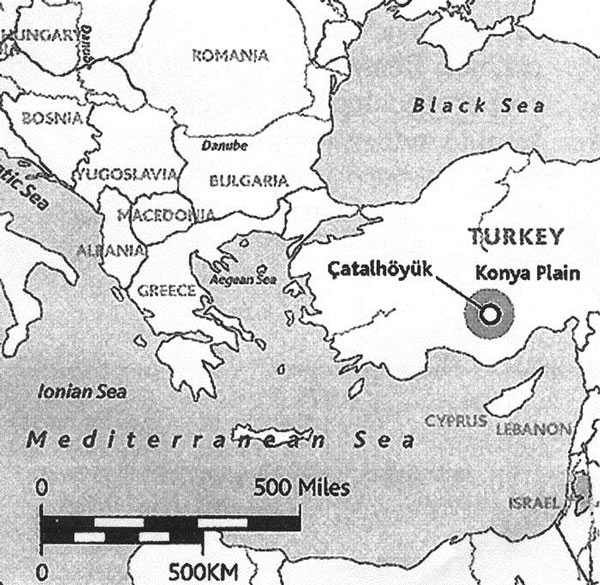
Items with the first mirror form were found in tombs in Asia Minor. In a settlement area dating from 6200 to 6000 BC, the Neolithic era in the Çatal Hüyük region, archaeologist Mellaart found the first mirrors. The current excavation area belongs to the cemetery of Konya, southern Turkey.
These mirrors are made by obsidian polishing (volcanic glass, ice casing) and have a circular or conical reflective surface. Although the reflection surface is slightly convex but still polished intentionally. The diameter of each mirror is about 9 cm and it is remarkable that it can reflect the image quite well.

The first mirror was ground from volcanic glass
Archaeologists have affirmed: "These objects have been used as mirrors with full functionality of a reflective surface. It is an unquestionable thing. " Moreover, archaeologists find the mirror carefully attached to the wall of a grave. At the same time, based on the grave content in the grave, this is a tomb of women .
Asia Minor is an area with many corundum minerals and volcanic glass. Corundum (also known as grinding powder) is a natural material grinding and polishing machine with a hardness of 9 in the Mohs hardness scale, it can easily be used to polish other mineral forms.
The bodies made from volcanic glass were then taken from Asia Minor to other places used as spears, name heads, knives, axes, axes and jewelry. Therefore, it is perfectly reasonable to deduce that the volcanic mirrors are also from this Asia Minor region. Archaeologists also said that the mirrors have a rough surface, one is polished with grinding powder and leather.
In a recent report by Colin Renfrew, professor of archeology at Cambridge University, confirmed that about 6000 BC, Çatalhöyük was one of the regions with a population of up to 10,000 people. This is the center of agricultural development and language. If Professor Colin's prediction is correct, Çatalhöyük and, more broadly, Anatolia are the first to create the mirror of mankind.
Next mirrors
The mirrors from the next date are found in Egypt. Archaeologist William M, Flinders Petrie (1853 - 1942) argued that the stone slabs were used as mirrors in the pre-Egyptian era. Lilyquist archaeologists' records also indicate that water evaporates very quickly on these stones. Lilyquist also stated that in addition, ceramic bowls designed to be filled with water were clearly used as mirrors and were discovered in the Badari region with a seal of about 4500 BC. Items found at Badari also have traces of wood around which are predicted to be used as mirrors for mirrors.

The image carved on the wall at the tombs is related to mirrors
Archaeologists have also found relics of polished bronze mirrors dating from about 4000 to 3000 years BC in the Tigris-Euphrates valley (now the Iraq region). Starting from this point, archaeologists have also found the appearance of mirrors in other things, in papyrus documents, . in ancient areas of Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Levant.

A mirror artifact found in Egypt
Unlike the flat surface mirrors found initially, the next mirrors have a convex or concave surface. Convex mirrors should see large images in a small area of the mirror. The concave surface is used to enlarge the images to look at.
This stage mirrors people who are paired with mysterious abilities and are often used in sacrifices and sacrifices.
Mirrors in East and Central Asia, including China
Archaeologists think that mirrors in China are developed independently and have a different form than the ones in the West. They claim that the forerunners in China originated in Siberia in the regions of Andronovo, Karasuk, north of the Caucasus Mountains near the black sea.
In China, two mirrors were discovered in Xi'an, Qinghai dates back to 2000 years BC in the Qi culture. Following that, mirrors were also found at the tomb of Phu Hao, one of 60 followers of the Hien Hien king of the Thuong Dynasty, dating from 1300-1028 BC. Later, the mirror was limitedly used in China under the Eastern Zhou period (around 1045-771 BC).

Ancient artifacts found in the Phu Hao tomb
The mirrors at that time had a diameter of 6 to 12 cm, without decoration and were pierced with a raised hole in the center to hang the mirror up. The mirror of this period is usually made of copper or alloy of copper, so it has a thin size and quite high hardness. Evidence of subsequent mirrors is also found on the relics of the Silk Road, in ancient tombs and mentioned in ancient texts.
In this period, the mirror is also assigned to mystical abilities by people who see the past and the future, give astrological words and even see through the inside of a person. These characteristics are similar to human views of mirrors in Egypt and other ancient areas of the same contemporary.
Central and South America
Mirrors were also found in South America by archaeologists dating back to 1925 BC onwards. In Mexico, people found mirrors made and used by Olmec, Mayan, and Teotihuacan people of the Mayan culture.
In Southern Colombia and Northern Ecuador, the techniques of refining and polishing gemstones were developed under the culture of La Tolita (year 600-300 BC). In Peru, people also found mirrors made of crystal with a copper frame around them. In many other places in South America, archaeologists have also found mirror-shaped morphological relics built and used.

The mirror of the Olmec people found in South America
In 1125 to 130 BC in the Americas, Olmec people knew how to use metal to create mirrors. Commonly used materials are iron pyrite, obsidian, anthracite. The antiquities found are still on display at a museum in Mexico City in the United States.
In this period, mirrors were polished, some had a flat surface, but most mirrors were fabricated concave with focal lengths of 5 to 80 cm. According to the analysis, these mirrors are composed of: magnetite, hematite, iron pyrite. According to records found, mirrors are used to create fire, medicine, astrological divination and astronomy.
Romans with the first glass mirror and banned in the Middle Ages

Figure of mirrors of the Romans
Around the 1st century, the first glass mirrors were invented by the Romans . This is due to the invention of the glass blowing method at the beginning of the 1st century by the people who made Syrian glass. From the very first time they were created, many special qualities were given to the mirror without any object. Greek philosophers have advised young men to look in the mirror to keep their souls clean, away from temptations in life that can lead them to the wrong path.
In the Middle Ages, mirrors had completely disappeared because religions had suggested that people could use mirrors to search for demons and see the afterlife. Now, we must use polished metal pieces or a water surface to replace the mirror. The development history of the mirror has taken a step back due to the superstitious notions of humans of this era.
The return of the mirror from the 13th century
It was not until the 13th century that glass mirrors returned to the human world. At this time, it was found to put tin on glass . With the technology available, in the process of blowing glass, the glass maker will pour molten tin into a glass basin, after the tin cools, the worker will separate the tin plate and attach it to one side of the plate. fine. At this time, there was no way to complete the coating on glass.

Figure of a mirror maker in Venice
Three centuries later, in the 15th century in Venice, glass masters invented a new technique to create a flat mirror using mercury to coat the back of the mirror. They found a way to coated glass onto a flat surface of a mirror with a special procedure. In addition, the workers devised a method of mixing gold and copper into tin to form a special mixture to coat the mirror to allow for a more beautiful mirror image. Because of such a "special" use of the mixture, the cost to create an example at that time is comparable to building a large naval ship.
By 1675, George Ravenscroft, a glassmaker , invented a new generation of mirrors by adding lead oxide to a mirror-coated mercury mix that allowed for cheap production. Mirror development stops at mercury use during this period.

A palace decorated with magnificent mirrors
After that, the mirror began to be received and entered people's lives. However, by the 16th century, mirrors were still considered by some to be related to witchcraft and mysterious rituals . 200 years later in the 16th century, some Spanish and French spies used mirrors to encode and decode messages using the mirror-coding system invented by Leonardo da Vinci in the 15th century. mirrors become an important part of the invention of periscope. The type of glass used in espionage activities in the war to send confidential information without using human information.
Now, mirrors have become popular with the production of luxury frames for decoration throughout the palaces in Europe. This time the mirroring technique was still held by Venice glassmakers and provided primarily for aristocracy at extremely expensive prices. However, the secret of using mirror mercury was eventually discovered and spread by industrial spies to London and Paris in the 17th century. Finally, mirror factories in France industrialized the process. make mirrors with cheap prices that are suitable for everyone. Even so, mercury toxicity is still a big problem.
Modern mirror
Three types of basic mirrors
To date, there have been many types of mirrors manufactured to serve the different needs of life. But there are three basic types of mirrors:
Flat mirror : Currently, mirror type mirrors are the most widely used. It is used as a mirror, decorative mirror, rearview mirror, used in all kinds of telescopes, microscopes, binoculars.

Convex mirror : The convex mirror is a type of mirror that bulges out on the outer edge, the reflection near the edge has a wider angle than in the center, creating a smaller and virtual image than the real object. Therefore convex spherical mirrors have many uses that are often seen as rearview mirrors for vehicles, help us look closer and see more objects behind.
Concave spherical mirror : Concave spherical mirror or convergence mirror is a kind of curved mirror inward like the inside of a spoon.
Therefore, light will converge at a point in front of the mirror called focus. This creates a real image right in front of the mirror. When looking far away, the image seems to be upside down but if you get close to overtaking the focus, your image will be normal again and magnified.
Therefore, concave spheres are used in shaving mirrors, makeup used in the sun to focus sunlight energy to burn kiln boilers .
In addition, there are other less popular mirrors such as:
Two-way mirror : This is a mirror with a glass surface coated with a very thin material and very light reflection. When these faces are rotated toward the illuminated side, some light will reflect and others will pass through the other side.
This makes the person standing on the side of the face dark to see the other side of the light, but the bright side cannot see the dark side. This is the same as at night it is very difficult to look outside through glass doors if the lights turn on. This type of mirror is often used in police interrogation rooms, specialized protective car windows .
Non-reversing mirror: This type of mirror was created when John Derby invented in 1887. It consisted of two mirrors perpendicular to each other, not reversing the image of the mirror image.
Audio mirror : This is a large mirror built with giant concrete plates that reflect and distribute sound instead of light.
The British army used them before inventing as a radar system as a warning system against air attacks.
 The truth about the mysterious red-haired giant at Lovelock Cave
The truth about the mysterious red-haired giant at Lovelock Cave Inunaki Tunnel: The haunted road leading into Japan's 'village of death'
Inunaki Tunnel: The haunted road leading into Japan's 'village of death' The mystery of the phenomenon of human reflection before dying
The mystery of the phenomenon of human reflection before dying 6 mysterious phenomena, although science has been developed for a long time, still cannot be answered
6 mysterious phenomena, although science has been developed for a long time, still cannot be answered