Use bacteria against earthquakes
Bacillus pasteurii bacteria have the ability to turn sand into cement. US researchers have taken the initiative to use them to make a porous soil solid, protecting earthquake-proof buildings.
Bacillus pasteurii (Photo: playfuls)
When the earth shook, the sandy areas became almost liquid and the buildings located in these areas could not resist. To solve this problem, so far only measures have been taken to put epoxy resin in the soil to harden the soil. But this toxin has harmful environmental consequences.
Another researcher, Jason Dejon of the University of California, tested another method. It is the use of Bacillus pasteurii specialized in making calcite (calcium carbonate) that binds sand grains together. This species has been used to seal cracks in statues.
Researchers have demonstrated that by introducing this bacterium into sandy soils and nutrients and oxygen, a solid cylinder made of clay is created. This nontoxic therapy can be done before, even after building a house. The structure of the soil remains unchanged, only the empty space between the grains of sand becomes solid.
Researchers are currently at a wider scale of testing and are prepared to use an earthquake simulation centrifuge located at UC Davis University. Some similar machines are available in the US, Japan and Europe.
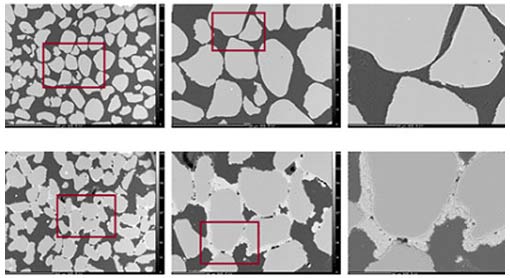
Bacillus pasteurii creates calcite ( calcium carbonate ) that binds sand grains together.
(Photo: Discovery)
NS
- Earthquakes caused many local shakes in Thua Thien Hue
- The most toxic and strange forms of bacteria on the planet
- Check out the types of polar bacteria that are beneficial to humans
- Recreate earthquakes in laboratories
- Earthquakes continuously shook northeast China
- What causes earthquakes and tsunamis?
- Earthquake in Japan and Ecuador involves
- Why do earthquakes in Nepal have great destructive power?
- Sichuan inspired more than 3,000 aftershocks
- The number of people killed by double seismic in China increased to 89
- Forget sharks, these 5 bacteria also make you
- How strong is the earthquake?
 Why do potatoes have eyes?
Why do potatoes have eyes? 'Tragedy' the world's largest carnivorous life: Death becomes ... public toilet
'Tragedy' the world's largest carnivorous life: Death becomes ... public toilet Tomatoes were once considered 'poisonous' for 200 years
Tomatoes were once considered 'poisonous' for 200 years Detecting microscopic parasites on human face
Detecting microscopic parasites on human face