Using artificial intelligence (AI) in the fight against cancer caused by asbestos
An international gene research experiment led by the University of Leicester has applied artificial intelligence (AI) to study a powerful form of cancer, the results of which could improve the patient's condition.
Mesothelioma is determined to be caused by inhalation of asbestos particles , where most affected are in the lining of the lungs or abdomen. Currently, there is very little chance of survival from asbestos infection, with only 7% of people surviving more than 5 years after diagnosis of asbestos infection, usually the median survival time is only about 12 to 18 months.
Currently, there is little chance of surviving an asbestos infection.
A new study by the University of Leicester's Mesothelioma Research Program has now revealed, using AI analysis to study the DNA sequences of mesothelioma tumours, that These cancer cells grow in a similar or repeated direction between cells. Based on this, it is possible to predict the degree of aggressiveness and appropriate therapy for this incurable cancer.
Professor Dean Fennell, Chair of the Department of Thoracic Medical Oncology at the University of Leicester and Director of the Leicester Mesothelioma Research Program, said: "It has long been found that asbestos is the cause of mesothelioma , however how this occurs is still a mystery. Using AI to look at genomic 'big data', this work will show us how mutated mesothelioma tumors orderly develop. This makes it possible to predict how long a patient might survive to recommend the most appropriate treatment – something Leicester aims to do through its clinical trial initiatives.
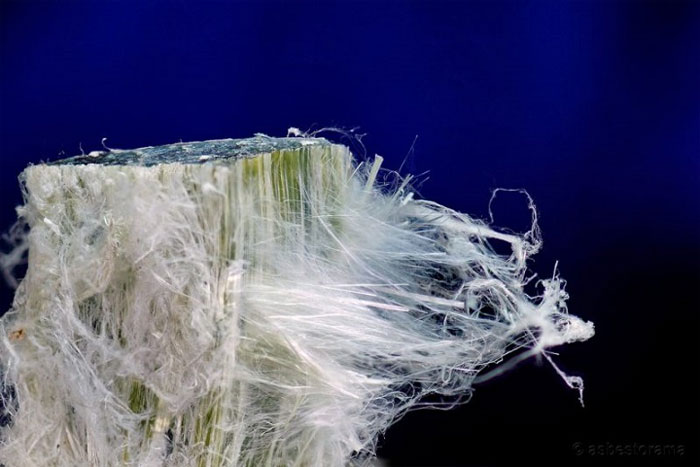

Asbestos is the cause of mesothelioma.
Despite the now banned use of asbestos and a series of strict regulations on its use - around 25 people are diagnosed with mesothelioma each year in Leicestershire and 190 in the UK. East Midlands. Mesothelioma cases in the UK have increased by 61% since the early 1990s. Until recently, chemotherapy was the only licensed option for treating patients with mesothelioma. However, treatment becomes limited when the patient stops responding to the drug.
Professor Fennell in collaboration with the University of Southampton recently made a major breakthrough in the treatment of the disease, demonstrating that the use of an immunotherapy drug called nivolumab increases survival. and stabilize the patient. This is the first trial to demonstrate improved survival in patients with recurrent mesothelioma.
- Artificial intelligence will contribute to defeating cancer
- Asbestos pain of Asia
- IBM's artificial intelligence invented new perfumes
- Diagnosis of cervical cancer faster by artificial intelligence
- Google's AI determines breast cancer more accurately than doctors
- Artificial intelligence predicts the progress and spread of cancer
- There will be 6,600 cases of cancer if using asbestos by 2030
- What is Artificial Intelligence? What is AI (artificial intelligence)?
- Artificial intelligence diagnoses breast cancer 30 times faster than a doctor
- Use artificial intelligence to detect cancer for only $ 1
- WHO sends a letter to the Prime Minister proposing to ban asbestos
- China wants to dominate global artificial intelligence
 The world's first sexless AI voice
The world's first sexless AI voice This cool t-shirt will make you invisible to AI
This cool t-shirt will make you invisible to AI AI can predict personality only through selfie photos
AI can predict personality only through selfie photos The world-famous chess player lost to Golaxy before, artificial intelligence 'made in China'
The world-famous chess player lost to Golaxy before, artificial intelligence 'made in China'