Earth is about to lose the Moon?
Does the Asteroid 2005 YU55 asteroid in size equivalent to 4 football fields can plunge into the moon and destroy the "Earth's satellite" ?
>>>Large asteroids fly over the Earth in the Fall
The YU55 will fly across Earth and the moon on November 8 (GMT) and is only about 325,000 kilometers from Earth, right inside the moon's orbit. In the past 35 years, there has not been a large meteorite that has strayed to Earth.
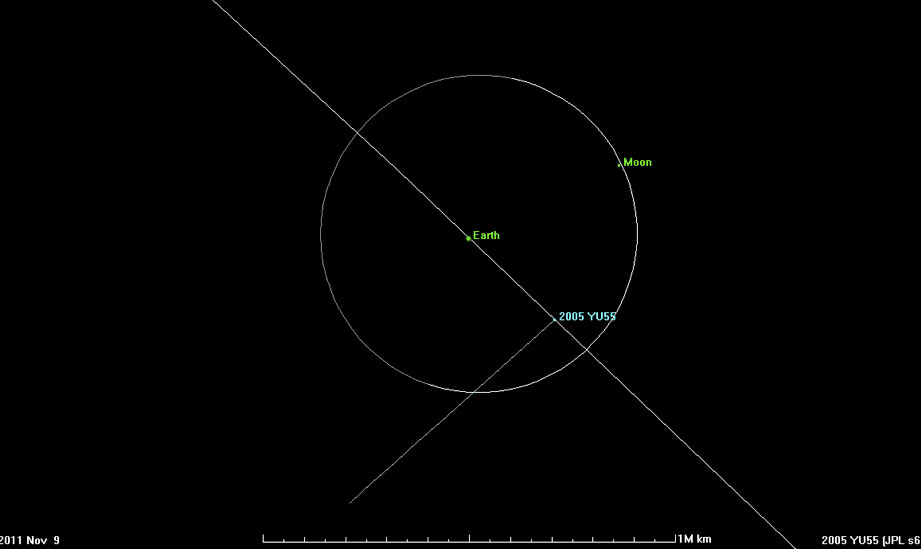
The asteroid's pathway cuts through the Earth and the moon.
NASA has reassured the world that 2005 YU55 is not dangerous to Earth, but its loyal companion - what about the moon?
Don Yeomans, director of NASA's Near-Earth Object Tracking Center (NEOP), confirmed that 2005 YU55 will not hit the moon. When the asteroid flies over the moon at a speed of 13 km / sec, the moon has traveled about half its journey around the earth and is on the other side of the Earth. These two objects will be 240,000km apart.
However, some curious readers still want to know, what will happen if 2005 YU55 clashes with the moon? Is the collision large enough for the moon to be destroyed?
Every 100,000 years
Speaking on Life's Little Mysteries , Yeoman said, sure, the moon will be greatly affected. The moon will not move, but a large wormhole will appear, at least 4 km in diameter. However, this wormhole is still "nothing" compared to the biggest moon on the moon today, still known as the Southernmost basin - Aitken with a diameter of 2500km.

According to LiveScience , a meteor of a size as large as 2005 YU55 must be 100,000 years threatening the Earth once. Because of its much smaller size, the risk for the moon is several hundred thousand years. Only, because the moon has no atmosphere, erosion and tectonic activity, all the collisions that it has encountered are still imprinted on its surface.
Suppose this 400m-diameter asteroid hits the moon, it will produce a large enough dust (and this dust moves at a rate large enough) to escape the moon's gravity, moving towards Earth. . And although most dust particles will burn when falling into the atmosphere, some dust can still escape to the ground.
In order for an asteroid to completely destroy the moon, covering the earth with a giant moon dust, it must be as big as the moon. Currently, NASA has not recorded any such large meteorite. The largest near-Earth asteroid is only about 8 km in diameter, Yeomans said.
- The moon is separated from Earth?
- Photo: Manually watch the biggest moon in 20 years
- Does the Moon have its own moon? And you will be surprised with its name!
- At the time of dinosaurs, volcanoes on the Moon used to work?
- What happens if the Moon falls to Earth?
- 'Super moon' is about to appear
- The Moon will collide with the Earth after 65 billion years
- Decode the phenomenon of the moon
- The Earth's Moon is a giant platinum storehouse?
- New hypothesis about the origin of the Moon
- 50 interesting facts about the moon
- The violent evolution of the Moon
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people