The taste changes with the temperature
Some tastes may vary depending on the ambient temperature. That is the conclusion drawn from the study published in Chemosensory Perception, conducted by Dr. Gary Pickering and fellow Brock University (Canada).
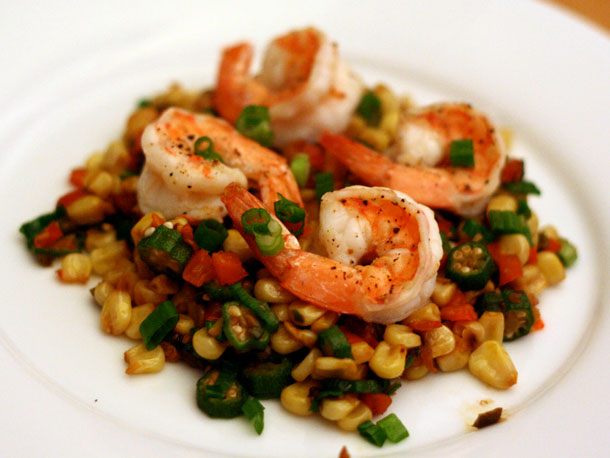

Accordingly, changes in temperature in food and food affect the concentration of acidity, bitterness and taste (making the mouth rough and dry as when eating peanuts and lentils). However, sweetness is not changed under hot and cold conditions.
Experts have tried to treat the food under 5 degrees Celsius, the ideal temperature to keep it cool, or to heat it at 35 degrees Celsius. Then the volunteers tasted two foods.
The results show that both sour and sour taste becomes darker at high temperatures, and the consistency lasts longer when eaten with chilled drinking water. Bitter taste also becomes more bitter in cold conditions.
For a minority of people, called "temperature takers" , the cold itself is a special taste.
In people who "taste temperature", which accounts for 20-30% of the population, hot or cold 'tasting' areas on the tongue surface create a characteristic flavor without the presence of food. And they have the ability to taste food and drinks better than ordinary people.
- Why does the taste of food vary when it is cold and hot?
- The taste is in a scientific perspective
- Taste of sensitive women than men?
- Can taste taste affect life?
- Deceptive devices taste better
- Discover the 6th taste of humans
- Obesity changes taste?
- New discovery: Human tongue can feel the taste of water
- The device simulates the taste of food on the screen
- The unexpected impact of taste and smell
- Miraculous fruits in Vietnam can turn every taste into sweetness
- Water does not taste tasteless, how do we feel?
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking Scientists create a durian-flavored lollipop in virtual reality
Scientists create a durian-flavored lollipop in virtual reality  New discovery on the cause of loss of smell because of Covid-19
New discovery on the cause of loss of smell because of Covid-19  New findings on loss of smell and taste when infected with Covid-19
New findings on loss of smell and taste when infected with Covid-19  The magic fork that can change the taste of food
The magic fork that can change the taste of food  Japan develops TV screen to help users taste food
Japan develops TV screen to help users taste food  Where is the taste of butterfly? The most accurate answer surprises you
Where is the taste of butterfly? The most accurate answer surprises you 