What should women with lupus do during pregnancy?
Lupus is an autoimmune disease, with no known cause, causing damage to all organs in the body. More than 90% of lupus cases occur in women of childbearing age. Therefore, the issue of pregnancy in this subject needs attention.
 In order to avoid serious complications, women with lupus should be pregnant in the midst of a medical condition (photo: att) Previously, doctors often advised that people with lupus should not become pregnant or if they were pregnant, they should quit, but now Because there are many advances in the diagnosis of pathogenesis as well as the introduction of many new immunosuppressive drugs, the therapeutic effect is higher.
In order to avoid serious complications, women with lupus should be pregnant in the midst of a medical condition (photo: att) Previously, doctors often advised that people with lupus should not become pregnant or if they were pregnant, they should quit, but now Because there are many advances in the diagnosis of pathogenesis as well as the introduction of many new immunosuppressive drugs, the therapeutic effect is higher.
Statistics show that, under close scrutiny by specialists, about 25% of pregnancies in lupus patients must give birth prematurely, 25% lose pregnancy. The rest are pregnant and give birth normally.
To avoid severe complications, female patients with lupus should be pregnant at the time of retreat, good health is less likely to develop a disease. If conception occurs while the disease is progressing or when kidney damage is present, the risk of an outbreak is very large. In fact, the number of pregnancies in women with lupus is lower than that of women without the disease. This is because these patients take long-term high-dose corticosteroids and some immunosuppressants, especially cyclophosphamide, which can cause a decline in fertility .
On the other hand, lupus also causes menstrual cycle disorders, so it also reduces the ability to conceive. During pregnancy there will be increased exacerbations of arthritis such as arthralgia due to ligaments, red rash due to vasodilation. Most exacerbations occur in the first 6 months of pregnancy or 2 months postpartum with mild symptoms such as fever, arthralgia, and rash should be easily controlled.
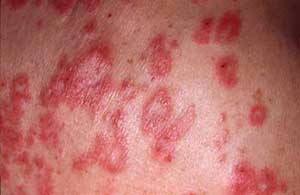
Lupus (Photo: emedicinehealth)
According to statistics, about 3% of lupus patients produce babies with lupus syndrome. This syndrome includes abnormal rash on the number of blood cells and arrhythmias. If there is no arrhythmia, the disease usually resolves after 3-6 months and does not leave sequelae.
One of the factors affecting the fetus in lupus patients is antiphospholipid antibodies. One-third of cases are in the blood of these antibodies . They create blood clots that clog the placenta, causing the placenta to not fully develop, hindering its normal functioning. As an intermediary transporting nutrients from the mother's body to the fetus, if the placenta is not fully developed, the fetus will be weak and grow slowly. The biggest risk in mothers with lupus is premature delivery. Babies born too young often have difficulty breathing, jaundice, anemia. However, in some modern neonatal resuscitation facilities, this situation can be resolved. For cases of premature or maternal hemorrhage or thrombocytopenia, the cesarean section will be performed. This is a safe method of getting pregnant for patients.
For pregnancies over 30 weeks old, weighing 1.5 kg can be raised and developed normally . These babies may be breastfed, but the mother should pay attention when taking hydroxychloroquine, azathioprine, and cyclophosphamide because these are drugs that can be excreted in milk and absorbed into the baby's blood, which can be toxic to children. Some other drugs can cause milk loss like prednisone. Some premature babies often do not have enough milk to suck, so they need to squeeze out and pump them to feed their babies. Ideally, lupus patients who are taking medication to control the disease should not breastfeed their babies.
To limit unwanted accidents that occur during and after pregnancy, the mother still has to use the medicines needed to control the disease. Non-placental drugs and fetal safety that mothers can use to control lupus during pregnancy are prednisone, prednisolone, methylprednisolone. Do not use ecotoxic drugs such as cyclophosphamide, but babies born with no risk of mental retardation or other birth defects. Do not use dexamethasone and betamethasone because these are drugs that can cross the placenta causing abnormalities to the fetus.
SCHOOL ORGANIZER
- Lupus, a dangerous disease that attacks young women
- Women with lupus should not become pregnant
- Why do women crave bizarre food during pregnancy?
- Lupus erythematosus - A dangerous little known disease
- 12 warning signs of lupus erythematosus
- Keep track of the entire magical pregnancy journey of women in 2 minutes!
- 1/4 of women are obese during pregnancy
- How to prevent pregnancy poisoning?
- First pregnancy is easy to miscarry the next time
- Women with diabetes during pregnancy are prone to miscarriage
- Pregnancy age and difference
- What the hell can happen: Women can continue to conceive even while pregnant
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking