Dangerous death from methanol in smuggled alcohol
The common methanol poison in illicit alcohol is just different from ethanol in the amount of carbon and hydrogen atoms but can be deadly in small doses.
Methanol is a popular synthetic alcohol commonly used in coolant and windshield cleaner, according to Live Science. Similar to ethanol, this alcohol is often found in alcohol, but methanol is toxic to the body. At the molecular level, it is only different from ethanol in that it contains less than one carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms, leading to different ways of treating the kidneys for two types of alcohol.

Methanol in illicit alcohol is highly toxic.(Artwork: Live Science).
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), liver metabolism begins when an enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase converts this chemical into another toxic chemical called acetaldehyde . Acetaldehyde is rapidly metabolized and will turn into non-toxic CO2 and water in just a few steps.
However, methanol metabolism is not so smooth. This chemical weakens the central nervous system in a way similar to ethanol. Therefore, if used in large doses, methanol can be as deadly as in normal alcohol poisoning, but NIH emphasizes only 56-27 grams of methanol is enough to kill an adult. This is because alcohol dehydrogenase converts methanol to formaldehyde.
The process is very slow, resulting in methanol poisoning symptoms sometimes only appear after hours or days. As soon as the sign of poisoning occurs, chemical reactions take place very quickly, creating the final product of formic acid, the chemical that is slowly metabolized in the bite of ants.
Formic acid accumulation destroys the optic nerve, which can lead to permanent blindness and even death if not detected promptly.
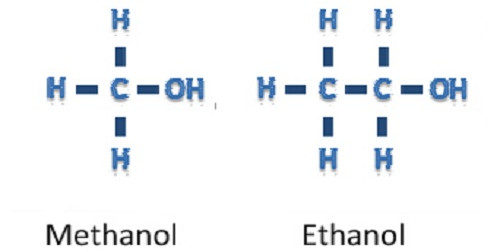
Chemical formula of methanol and ethanol.(Photo: Wordpress).
Due to its toxicity, methanol is sometimes added to industrial ethanol products, such as solvents, to eliminate their ability to make drinks. By adding methanol, producers can avoid taxes applied to alcoholic drinks and sell products at cheaper production costs.
Some unlawful and irresponsible businesses often give alcohol to methanol because it is cheaper than ethanol. In addition, unintended high levels of methanol can inadvertently be created during fermentation of drinks with high levels of pectin, such as drinks made from grapes and strawberries. During proper fermentation, methanol is produced at a low and safe level. However, bacteria cause methanol to be produced at higher levels in unhygienic containers.
- How will alcohol containing methanol
- Identify regular alcohol with industrial alcoholic alcohol methanol toxic
- How is methanol - an extremely toxic substance in alcohol destroying the body?
- The primary way to save methanol poisoning
- The 49-person Russian shower gel when drinking alcohol instead
- How to use alcohol stove for safety?
- Use alcohol to study the school from the universe
- Checks can measure alcohol content in a full bottle
- The catalyst helps produce methanol directly from carbon dioxide
- Gender preserves shock because of smuggling Thai rare turtles
- The antidote after drinking alcohol
- Vehicles die constantly when running on methanol gasoline
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking Dangerous when drinking and using alcohol 90 degrees of antiseptic
Dangerous when drinking and using alcohol 90 degrees of antiseptic  Use alcohol to study the school from the universe
Use alcohol to study the school from the universe  Vehicles die constantly when running on methanol gasoline
Vehicles die constantly when running on methanol gasoline  The new catalyst produces methanol from CO2
The new catalyst produces methanol from CO2  How will alcohol containing methanol
How will alcohol containing methanol  Identify regular alcohol with industrial alcoholic alcohol methanol toxic
Identify regular alcohol with industrial alcoholic alcohol methanol toxic 