The primary way to save methanol poisoning
In the past few days, in the whole country, there have been many poisoning cases due to drinking methanol alcohol, many people have died. Although not fatal, the consequences of methanol alcohol poisoning are still very heavy: The patients can damage the brain, optic nerve, brain necrosis like those of severe strokes, add love Organ injury. How is methanol dangerous for the body and how is first aid and emergency poisoning of methanol alcohol? . The doctor's article helps you read more and actively prevent it.
What is methanol?
Methanol is a liquid chemical and a source of energy derived from natural gas, coal, bio-waste and CO2. Widely used as chemical materials and applications for clean energy for the environment (transport fuels, marine fuels, solar batteries, electricity generation, cooking .); Methanol is the simplest form of alcohol, is a mild, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic flavor very similar to ethanol (drinkable alcohol). Methanol is a by-product of alcohol distillation and is the first liquid to condense when alcohol is cooked in traditional distillation. However, unlike ethanol, methanol is highly toxic and unsuitable for drinking. Pure methanol has a faintly sweet smell at ambient temperature; Raw methanol may have a pungent, unpleasant odor. Methanol is widely used in industrial paints, paint remover and solvents. It is also used in the production of formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl and inorganic acid derivatives; as an antifreeze, fuel freeze inhibitor and increased octane fuel index; an ethanol denaturing agent; a solvent that extracts and makes fuel for picnic and gas cookers.
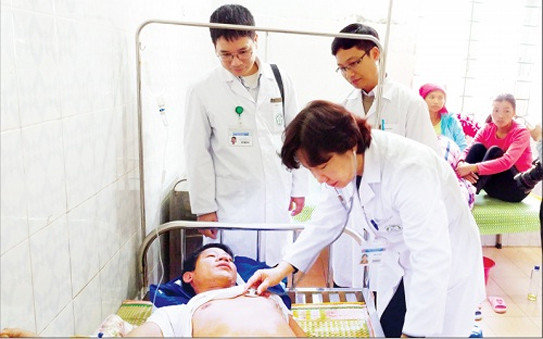
The doctors of Bach Mai Hospital were present in time to assist Lai Chau physician to treat patients with collective alcohol poisoning (photo taken on February 16, 2017).(Photo: The Anh).
When is methanol poisoning suspected?
After drinking smuggled or unidentified alcohol or accidentally ingesting methanol, showing severe headache, dizziness, shortness of breath or deep breathing, drowsiness is a warning sign of poisoning. These symptoms may last 12-24 hours after exposure.
Effect of methanol on the body
After entering the body, methanol is converted into formic acid by the body, which is much more toxic than methanol. Formic acid causes toxins to the nerve and retina. It can cause permanent damage to the central nervous system as well as the retina. High levels of formic acid can cause multiple organ failure, severe metabolic acidosis, and even death.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning:
- A lot of noise.
- Diarrhea or abdominal pain.
- Headache.
- Low blood pressure.
- Dizziness or disorientation.
- Lips and nails are purple.
- Aggressive behavior.
- Look unclear or blurred, blind.
- Shortness of breath.
- Convulsions.
- Coma and death.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning usually appear within 30 minutes after ingestion but may be later depending on the amount that the patient takes, whether or not the patient drinks with ethanol (slower symptoms appear). There are usually two stages, the discreet stage (hours to the first 30 hours) and the stage of clear poisoning following. Because the initial symptoms are usually discreet and mild (mild nervous depression, sedation, anesthesia), they are often subjective and ignored by patients.
First aid for people suspected of methanol poisoning
To give first aid to people suspected of methanol poisoning, first of all, you must follow first aid methods for poisoning patients. You can only do so under the direction and assistance of medical personnel or after calling the Poison Center or the methanol poisoning counseling hotline to be directed by specialized staff.

First aid for alcohol poisoning patients in Lai Chau.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended methanol poisoning: " The main treatment principle for methanol poisoning is to further prevent the metabolism of methanol, overcoming abnormalities of the Metabolism and other supportive care Metabolism may be prevented by administering ethanol or fomepizole, which may include the control of acidosis with sodium acid carbonate, tube placement. and mechanical respiration and the use of excretion as a dialysis method ".
The only definitive treatment for methanol poisoning is hemodialysis . Hemodialysis helps maintain the body's chemical balance - including substances like potassium, sodium and chloride and helps control the patient's blood pressure. Therefore, if methanol poisoning occurs, it is necessary to arrange for immediate transfer of patients to a large hospital with hemodialysis equipment. This is an extremely important time for emergencies that threaten the lives of patients.
Measures to handle at the grassroots level
Managing patients with methanol poisoning is like managing an emergency patient in general.
- Quickly remove toxins and use specific antidote if available.
- Resuscitation of living functions. When clinical symptoms appear, resuscitation measures become of prime importance.
- Resuscitation should be performed immediately prior to the elimination of the toxins and for the safe elimination of toxins, especially to ensure stable breathing and circulation.
- Call the nearest poison control center for assistance.
In adults , methanol poisoning at a dose of 8g (1ml of 100% solution) can cause blindness, poisoning at a dose of 10g (30ml of 40% solution) can be fatal.
In children , methanol poisoning at a dose of 0.25ml / kg caused blindness and 0.5ml / kg was fatal (100% solution).
Before poisoning, methanol is converted into formaldehyde and then oxidized to formic acid (formate). High levels of formic acid in the blood inhibit mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase in cells causing cellular oxygen deficiency, severe metabolic acidosis, optic nerve damage and eye retinal damage. In addition, methanol causes CNS suppression, vasodilation, hypotension and reduced cardiac output.
- The 49-person Russian shower gel when drinking alcohol instead
- How is methanol - an extremely toxic substance in alcohol destroying the body?
- Dangerous death from methanol in smuggled alcohol
- Identify regular alcohol with industrial alcoholic alcohol methanol toxic
- How will alcohol containing methanol
- The catalyst helps produce methanol directly from carbon dioxide
- The new catalyst produces methanol from CO2
- Checks can measure alcohol content in a full bottle
- Measures to handle when food poisoning at home
- What to eat when suffering from food poisoning
- Vehicles die constantly when running on methanol gasoline
- How to deal with drug poisoning
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking Dangerous when drinking and using alcohol 90 degrees of antiseptic
Dangerous when drinking and using alcohol 90 degrees of antiseptic  Use alcohol to study the school from the universe
Use alcohol to study the school from the universe  Vehicles die constantly when running on methanol gasoline
Vehicles die constantly when running on methanol gasoline  The new catalyst produces methanol from CO2
The new catalyst produces methanol from CO2  How will alcohol containing methanol
How will alcohol containing methanol  Dangerous death from methanol in smuggled alcohol
Dangerous death from methanol in smuggled alcohol 