New weight loss device to fight anxiety
People with obesity have a new useful device in fighting their excess weight. The device works by transmitting electrical impulses to nerves that determine the feeling of hunger and fullness between the brain and the stomach.
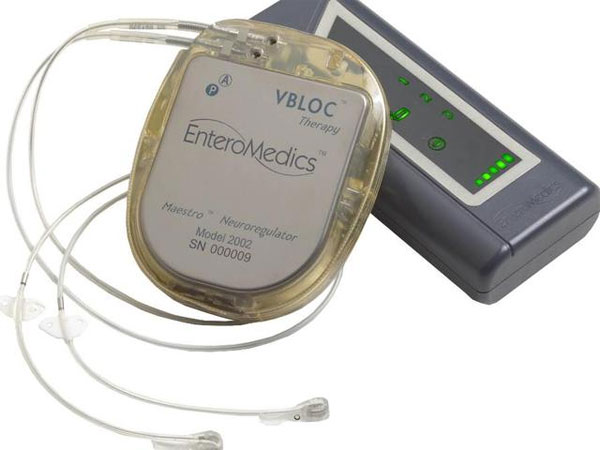
Maestro system
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a medical device called the Maestro Rechargeble System that is implanted in the stomach and through an adjustable controller from outside. , help obese people lose weight. This device is applicable to patients 18 years of age and older, and older people with body mass index (BMI) of 35 to 45. People with symptoms of obesity-related diseases such as diabetes Type 2 cannot lose weight through traditional methods that can rely on this device.
Obesity is rising at an alarming rate not only in developed countries but also in developing countries.
The Maestro system targets the nerve pathway that determines the feeling of hunger and fullness between the brain and the stomach. The device includes a rechargeable electric pulse generator, surgical leads and electrodes implanted in the abdominal area. It works by transmitting electrical impulses to the axes in the abdominal region of the vagus involved in controlling gastric emptying and telling the brain that the stomach is empty or full. The external controller allows patients to charge the device and medical professionals adjust the device to obtain optimal treatment and minimize side effects.

Electric pulse generators aim at nerves that determine feeling of fullness and hunger, limiting the appetite desire of obese people
In a clinical trial, patients using this device lost 8.5% more body weight than those who did not use it. Approximately 53% of patients using the device reduce at least 20% of excess weight and 38% of patients reduce by at least 25%.

With this device, obese people are no longer "suffering" when choosing between "eating" or "not eating".
However, if compared to slimming surgery, the effectiveness of this device is not really impressive. Eric T. Volckmann, a specialist in slimming surgery at the University of Utah Health Care, said that after gastric surgery, patients can reduce 60% to 80% of the body's excess weight.
Besides, serious side effects reported in clinical trials of this device include nausea, vomiting, pain in the neuropathic region and complications after surgery. Other side effects include pain, heartburn, difficulty swallowing, belching and chest pain.
- Special weight loss device helps prevent appetite
- Lose weight but just drink each water? Is it true that life is just pink like that?
- What happens after the weight loss plan?
- One-sixth of the US population struggles with weight loss
- The world's first weight loss shirt
- Obesity control device
- Write to reduce fat
- Weight loss surgery can weaken bones
- The injection helps reduce 6.5kg in 1 month: the future without fasting is still thin here!
- Extremely simple measures to help control weight effectively
- Why do you stop dieting and gain weight?
- Worried about the higher IQ?
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking