What do the fruits look like before being tamed by humans?
Over thousands of thousands of people, with breeding techniques, people have created crops that are far from their ancestors.
According to Science Alert, unlike genetic modification (GMO), the technique directly connects genes from other organisms (such as bacteria) to plants to create desirable traits, such as pest resistance, select Breeding is a slower process. Farmers must choose varieties and cultivate crops over time. To date, many fruit and food crops have been far removed from their ancestors.
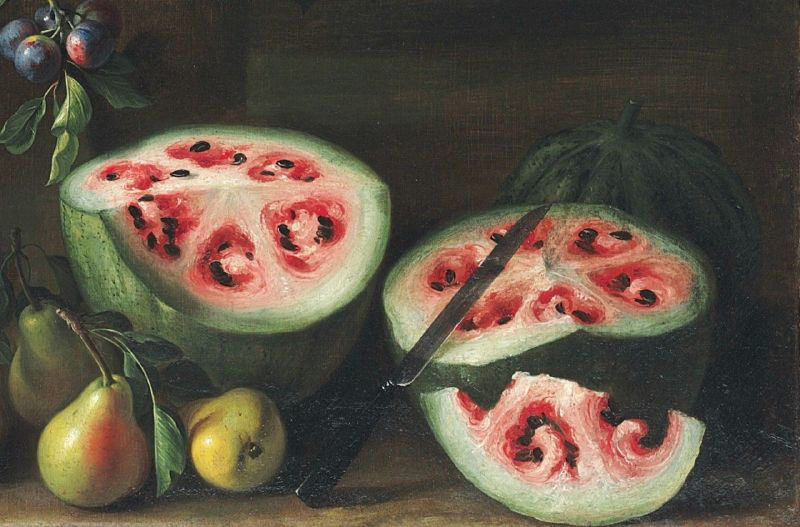

This is Giovanni Stanchi's 17th-century watermelon painting, very far from today's watermelon. From the cut of the melon it can be seen that its internal structure consists of 6 vortex triangles.Although there is a suspicion that this may be unripe or dried melon, but if you look at the black color of the seeds, you can see that this is a ripe melon painting.(Photo: Wikimedia Commons)
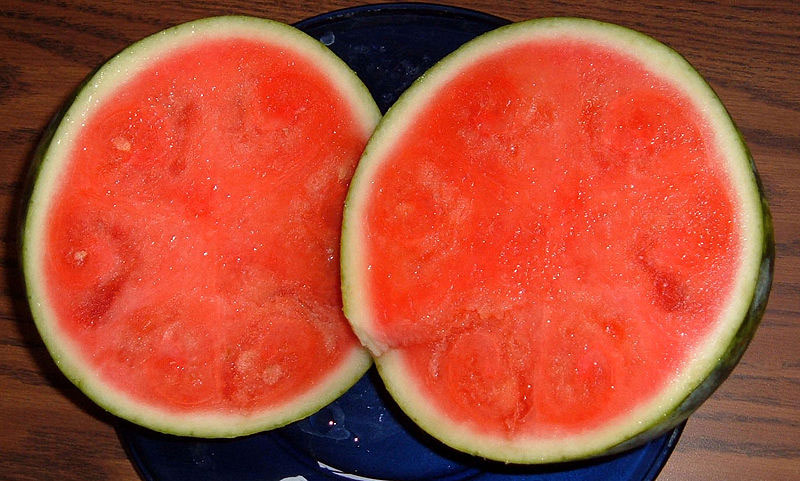
Over time, humans created watermelon varieties with bright red flesh and flesh, as shown in the picture, even with seedless watermelons.(Photo: Scott Ehardt / Wikimedia)
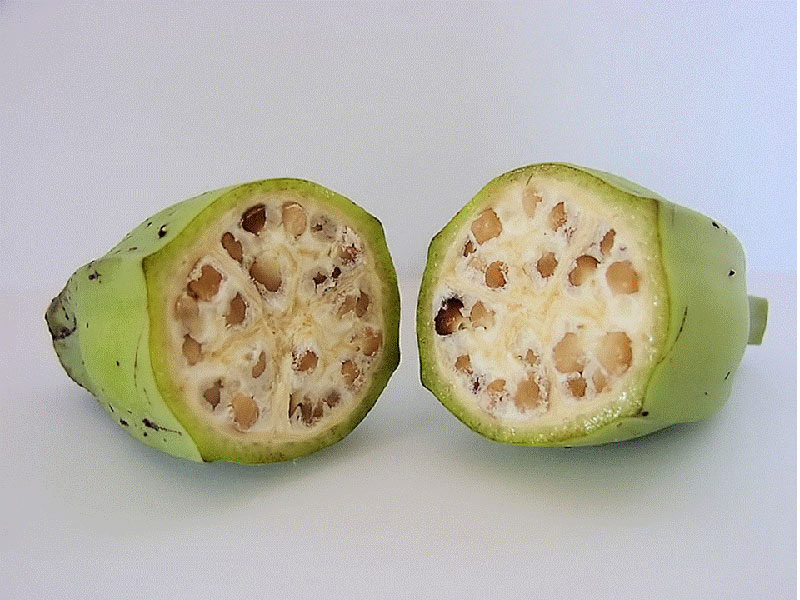

Bananas can start growing 7,000 to 10,000 years ago, in what is today Papua New Guinea.They are also grown in Southeast Asia.Bananas today originate from two wild bananas, Musa acuminata and Musa balbisiana as shown in the picture.This banana variety has little meat, hard seed.(Photos: Wikipedia)
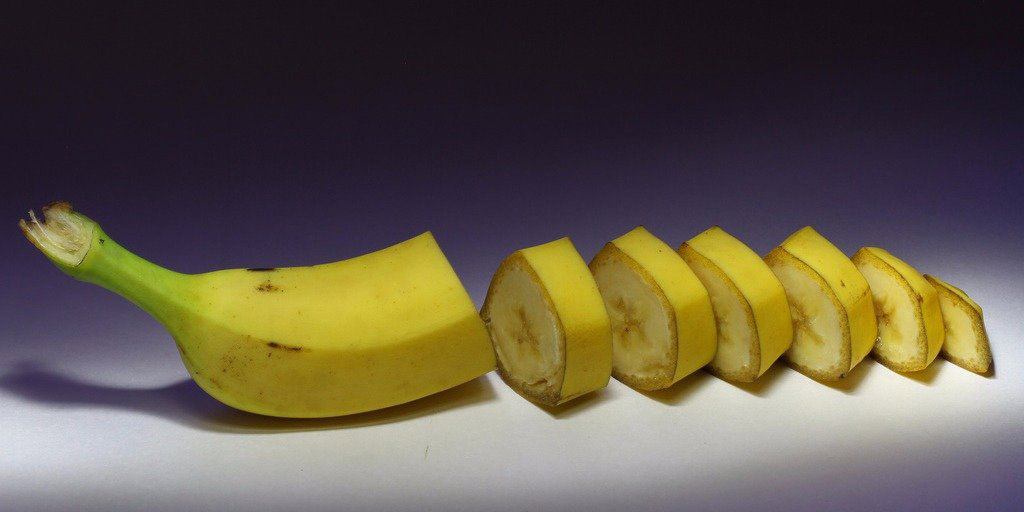

Banana today.(Photo: Domiriel / Flickr Creative Commons).Bananas today, with easy-to-hold shapes, peel off.Compared to ancestors, they have much smaller seeds, more delicious and more nutritious.

Wild eggplant. (Photos: Botanic Stories)
Throughout history, eggplant has many different shapes and colors, such as white, blue, purple, yellow.They are earliest grown in China.The original eggplant variety has thorns in the flower stalk.

Eggplant day right away. (Photo: YoAmes / Flickr)
The selection process has removed the thorns, giving us the bigger, elongated, purple eggplant fruits that can be found everywhere selling vegetables.

Wild carrots. (Photos: Genetic Literacy Program)
Carrots are known to grow earliest in Persia and Asia Minor, around the 10th century. Initially, their bodies were purple or white with small roots, dividing branches as shown.The purple part then changes to yellow.

Carrots today. (Photos: TTL media / Shutterstock.com)
Farmers have modified the small, white root carrots with a strong odor, two years of flowering once to become edible orange root carrots, harvested every winter.

Ancient corn. (Photo: Living Crop Museum)
The best example of the breeding process.The North American sweet corn variety is made from a type of teosinte plant that is almost impossible to use as food.The natural corn on the image began to be planted by humans around 7,000 BC, tasted like a dried potato, according to chemistry teacher James Kennedy.

Corn today. (Photo: Rosana Prada / Flickr)
Today, corn is about 9,000 years older than corn, about 1,000 times, easy to grow and peel.It contains 6.6% of sugar, compared with only 1.9% of ancient corn, according to Kennedy.This change began around the 15th century, when Europeans started growing corn.

Natural digging, 4,000 BC. (Photo: James Kennedy)
Natural peaches began to be planted by Chinese people around 4,000 BC, the fruit flesh was small, there was a place like earth, slightly salty, sour, sweet, according to Kennedy.

Digging today. (Photo: James Kennedy)
After thousands of years of breeding, peaches are 64 times bigger today, 27% more water and 4 times sweeter.
- 6 types of morning fruits are 'medicinal herbs' dinner is 'poison'
- Meaning of five fruits in 3 regions culture
- Revealing Chinese fruit
- This is the technology that helps the most delicious fresh fruit
- 'Rare rare summer fruits'
- How to wash fruits correctly to remove chemicals
- Emergent fruits when sick
- Notes to keep fruits and vegetables the most nutritious
- Simple way to identify Chinese vegetables and fruits
- The naked eye cannot distinguish between fruits with chemicals
- Drugs from wild fruits
- Why fruits ripen and flowers die
 The 11 most unique public toilets in the world
The 11 most unique public toilets in the world Explore the ghost town in Namibia
Explore the ghost town in Namibia Rare historical moments are 'colored', giving us a clearer view of the past
Rare historical moments are 'colored', giving us a clearer view of the past The world famous ghost ship
The world famous ghost ship